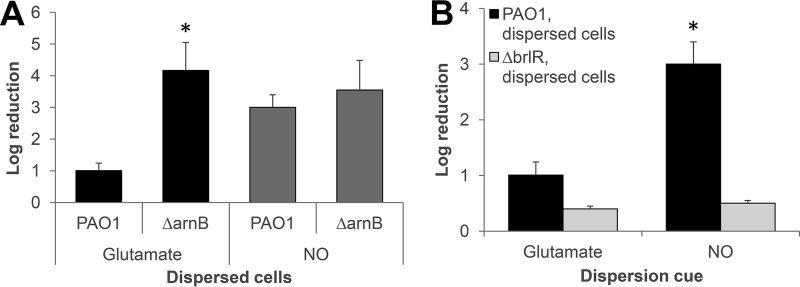
FIG 7.
The LPS modification system and BrlR contribute to the difference in the susceptibility phenotype of glutamate- and NO-induced dispersed cells to colistin. (A) Susceptibility of dispersed cells obtained from biofilms of wild-type and ΔarnB mutant strains in response to glutamate and NO to colistin (20 μg/ml) after exposure for 1 h at 37°C. (B) Inactivation of brlR coincides with dispersed cells being resistant to colistin (20 μg/ml) regardless of the dispersion cue used (glutamate, NO). Dispersed cells obtained after exposure of P. aeruginosa wild-type biofilms to glutamate or NO were used as a control. Colistin susceptibility is expressed as log10 reduction in CFU. All experiments were repeated at least three times. Error bars indicate standard deviations. *, Significantly different from PAO1 dispersed cells in response to same dispersion cue (P < 0.01 as determined by ANOVA and SigmaStat).