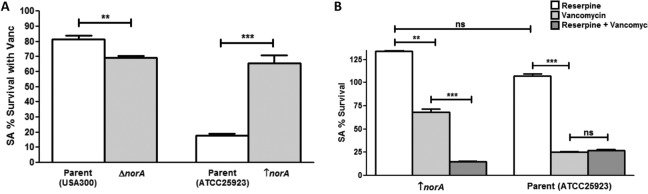
FIG 5.
Modulation of efflux pumps impacts the S. aureus response to vancomycin. (A) S. aureus mutant strains with modulated norA expression were tested in biofilm vancomycin susceptibility testing. Based on results from MTS viability assays, the mutant strain lacking the norA gene (ΔnorA; NE1034) displayed a significant decrease in survival with vancomycin compared to that of its parent strain (USA300). In contrast, the norA-overexpressing strain (↑norA; SA1199B) displayed a significant increase in survival compared to that of its parent strain (ATCC 25923). (B) However, when a chemical inhibitor of efflux pumps (reserpine) was included in the vancomycin susceptibility testing, the initially observed increased survival of the norA-overexpressing strain was completely abolished, with no effect of the inhibitor on the susceptibility of the parent strain to vancomycin. Reserpine alone did not affect S. aureus viability (**, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001; ns, not significant).