Figure 5.
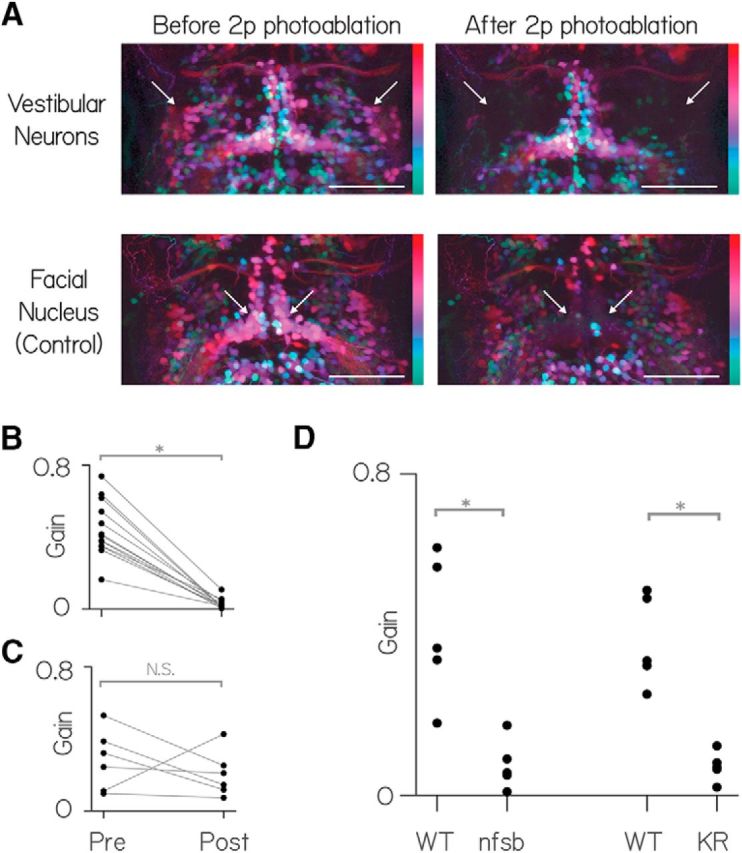
Vestibular nucleus neurons labeled in Tg(−6.7FRhcrtR:gal4VP16) are necessary for both nose-up and nose-down gaze stabilization. A, Horizontal MIP of vestibular and control neurons (nVII) in rhombomeres 4–8 in Tg(−6.7FRhcrtR:gal4VP16); Tg(UAS-E1b:Kaede)s1999t; Tg(isl1:GFP) fish before and after targeted photo-ablation of vestibular neuron cell bodies. γ = 0.5 highlights dim signal. Colors represent depth over ∼150 μm. White arrows indicate the general region of targeted cell bodies in either the vestibular nuclei (top row) or the facial nucleus (nVII). Scale bar, 150 μm. For anatomical localization, compare with the right side of Figure 1B. B, Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain preablation and postablation of vestibular neurons. C, Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain preablation and postablation of facial nucleus neurons. D, Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain wild-type siblings (WT) and fish with pharmacogenetic (nitroreductase, “nfsb”) and optogenetic ablation (Killer-Red [KR]) of neurons in Tg(−6.7FRhcrtR:gal4VP16).
