Fig. 2.
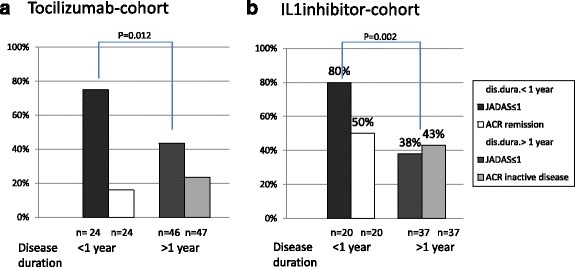
Juvenile Disease Activity Score (JADAS)-remission (JADAS-10 ≤ 1) and American College of Rheumatology (ACR) inactive disease (Wallace criteria) in patients in the tocilizumab cohort (a) and the interleukin-1 inhibitor (IL-1i) cohort (b) split according to disease duration <1 year and >1 year. At the last report in the early-treated cohort, 18 patients (75%) on tocilizumab and 16 (80%) on Il-1-inhibitors reached JADAS-remission significantly more frequently (OR 3.9 (95% CI, 1.3–11.6); p = 0.012 for tocilizumab and OR 6.6 (95% CI, 1.8–23.7; p = 0.002 for IL-1i) compared to 20 (44%) and 14 (38%), respectively. No difference was noted in the rate of patients reaching ACR inactive disease. Data are expressed as observed. The number of patients contributing to the calculation is given below the figure
