Figure 4. Cell type-specific aptamer-functionalized nanocarriers for targeted therapy.
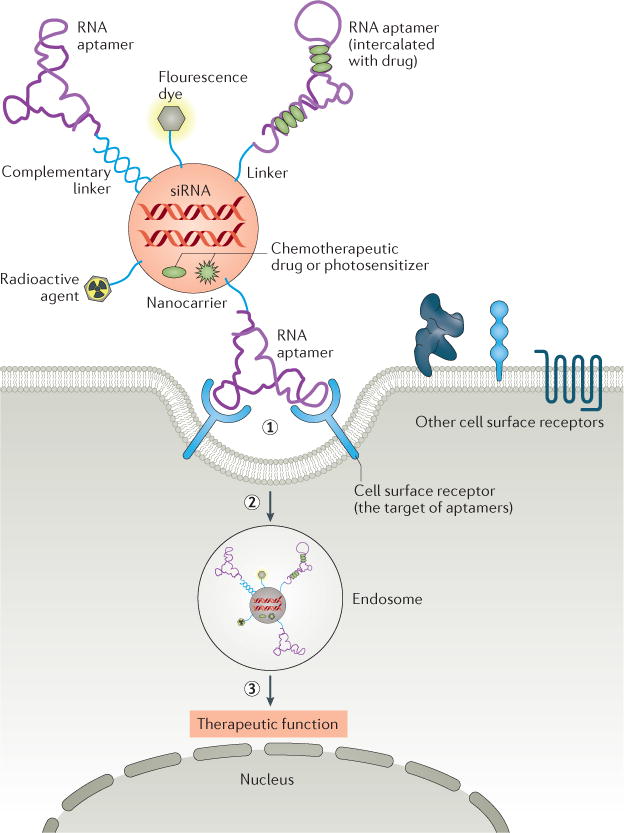
Multiple components such as therapeutics (therapeutic oligonucleotides, chemotherapy agents), actively targeting agents (cell type-specific aptamers), and imaging agents (fluorescent dyes or radioactivity agents) are rationally assembled in one nanoscale carrier to achieve multifunctional nanomedicine. (1) Upon binding of the aptamer portion of nanocarrier conjugate to the target receptor on the cell surface, (2) the conjugate is internalized into cells, probably through a receptor-mediated endocytosis pathway. (3) It is presumed that the conjugate shuttles into the endosome; subsequently, the therapeutic agents dissociate from the complex and escape the endosome. The released therapeutic agents mediated therapeutic function.
