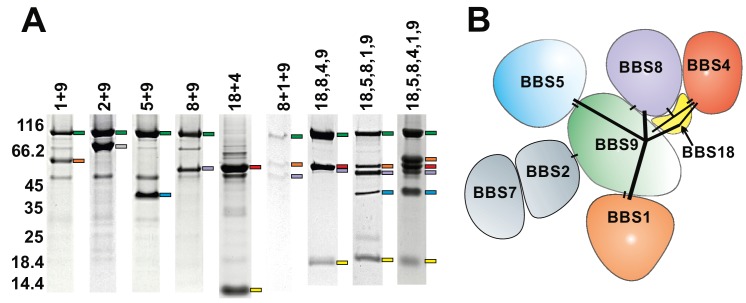
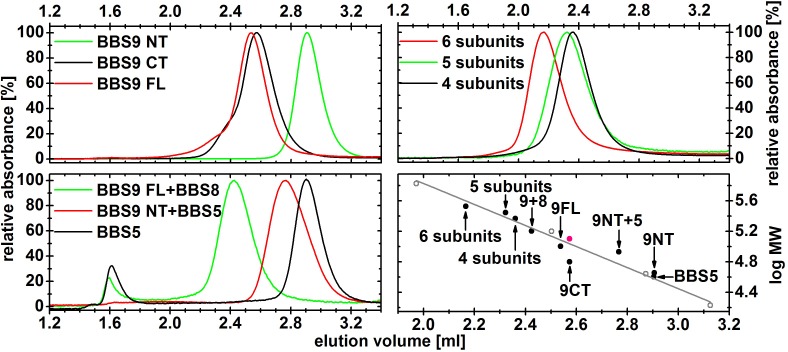
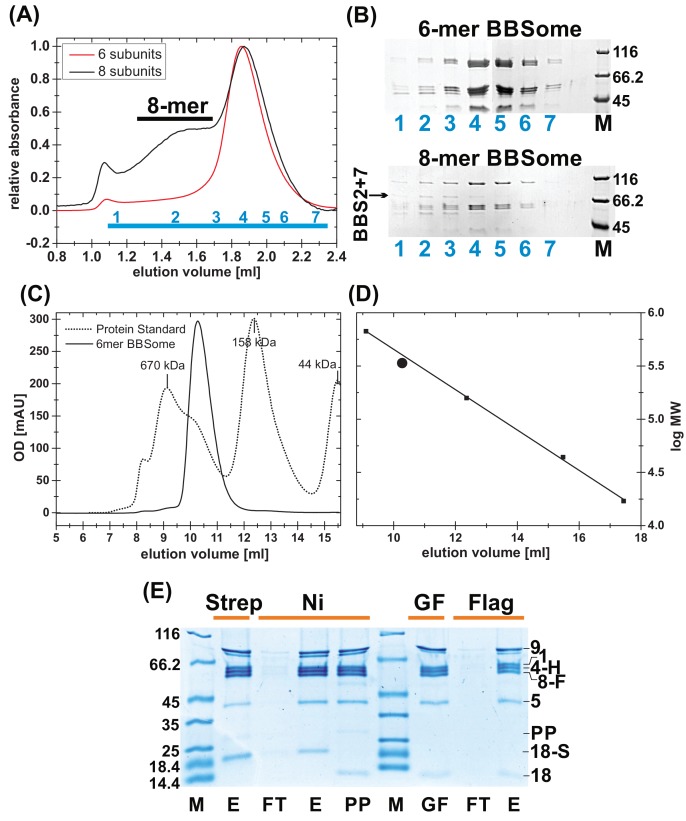
Figure 1. Subcomplexes of the BBSome.
(A) Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE of binary and multimeric BBSome complexes purified by Strep/Flag tandem affinity purification. The BBS proteins are indicated with color-coded marks. Variances in gel mobility of the individual components is caused by different affinity tags, as is most pronounced for BBS18. (B) Schematic subunit organization model that is consistent with expression and stability of subcomplexes (Components of the most stable core complex in color, and the two missing subunits in grey).