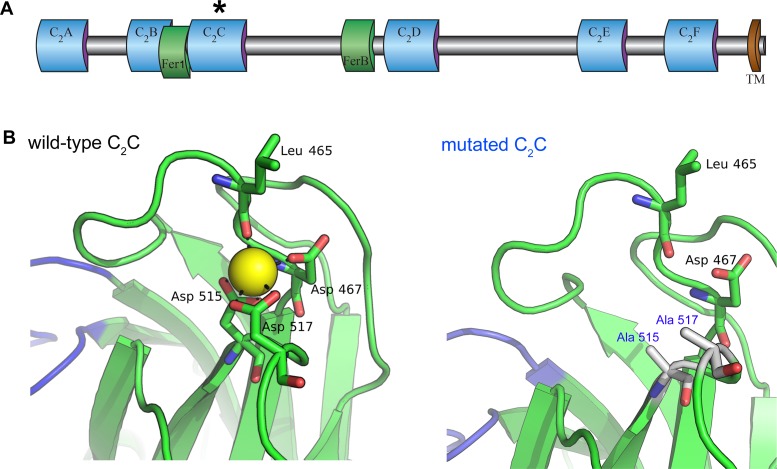
Figure 1. Homology model of the otoferlin C2C domain.
(A) Predicted domain structure of the otoferlin protein. Otoferlin is a transmembrane vesicular protein (1997 amino acids in the mouse) consisting of six C2 domains (C2A-F), one Fer1 domain, and one FerB domain (central domains of still unknown function in proteins of the ferlin family) in its extravesicular (i.e cytoplasmic) portion. The asterisk indicates the C2C domain targeted for mutagenesis. (B) Ten candidate models were calculated with MODELLER (Webb and Sali, 2014), based on the X-ray structure of the human dysferlin C2A domain (4ihb) (Fuson et al., 2014). The primary sequence identity between dysferlin C2A and mouse otoferlin C2C, assuming type II C2 domain topology, is 23%. The model with the lowest energy score was selected for analysis. Further refinement was performed with ModRefiner (Xu and Zhang, 2011) using dysferlin C2A as the structural reference. At least one Ca2+ ion (yellow sphere) could be modeled in the C2C domain of otoferlin. The position and coordination of this ion within the putative divalent cation binding pocket of the homology model was refined by simulating 20 ns of molecular dynamics using NAMD (Phillips et al., 2005).