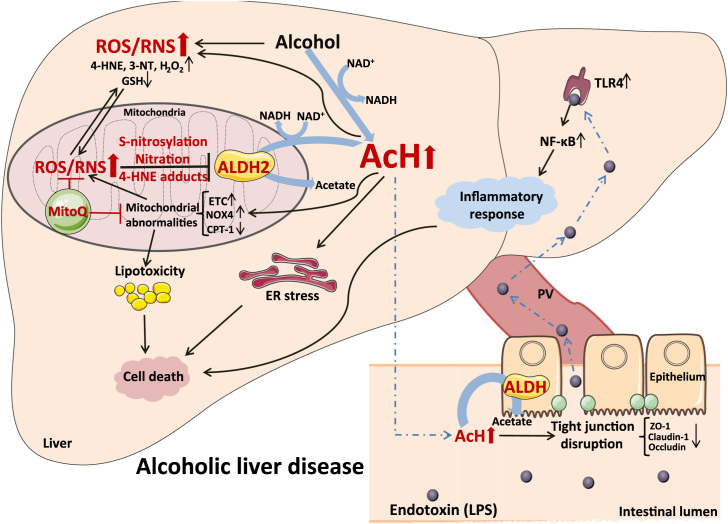
Fig. 8.
Depicting the possible molecular mechansims by which MitoQ prevents alcoholic liver disease through modulating ALDH2 posttranslational modifications. After chronic alcohol abuse, oxidative and nitrosative stress were increased, which impaired mitochondrial ALDH2 activity via cysteine S-nitrosylation, tyrosine nitration and 4-HNE adducts formation. Acetaldehyde accumulated in the system result in ileal tight junction disruption and increased plasma endotoxin and subsequently inflammatory response in the liver. Excess acetaldehyde accumulation in the liver leads to enhanced lipotoxicity, ER stress and cell apoptosis pathway activation. MitoQ supplementation prevented alcohol-induced ALDH2 posttranslational modifications and accelerated acetaldehyde clearance, which against alcohol-induced pathogenesis at the gut-liver axis.