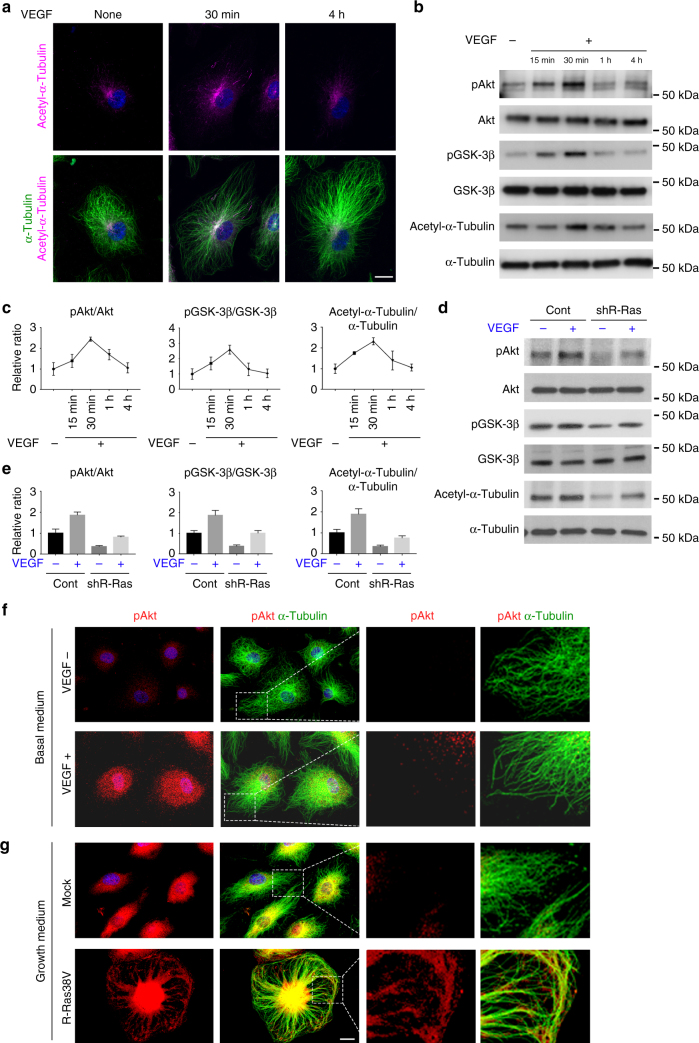
Fig. 3.
VEGF and R-Ras signaling exert differential effects on Akt and microtubule. ECs were cultured in low-serum basal media (2% horse serum without growth factor supplements) for overnight and stimulated with (+) or without (−) 50 ng/ml VEGF-A for indicated time. Akt (Ser473) and GSK-3β (Ser9) phosphorylation and α-tubulin acetylation were analyzed by immunofluorescence (a) and/or western blot (b). c Levels of phosphorylated Akt, GSK-3β, and acetylated α-tubulin were quantitated by densitometry and normalized to the corresponding total protein levels. d Control or R-Ras-silenced ECs were stimulated with VEGF-A, and Akt/GSK-3β phosphorylation and α-tubulin acetylation were analyzed. e Western blots of phosphorylated Akt, GSK-3β, and acetylated α-tubulin were normalized to corresponding total protein levels. f, g Immunofluorescence of phospho-Akt (red) and total α-tubulin (green). ECs were cultured in basal media and stimulated with (+) or without (−) 50 ng/ml VEGF-A for 30 min (f). Mock or R-Ras38V-transduced ECs (g). Higher magnification of the boxed area is also shown. The graphs show the combined results of at least three independent experiments. Scale bars, 20 µm