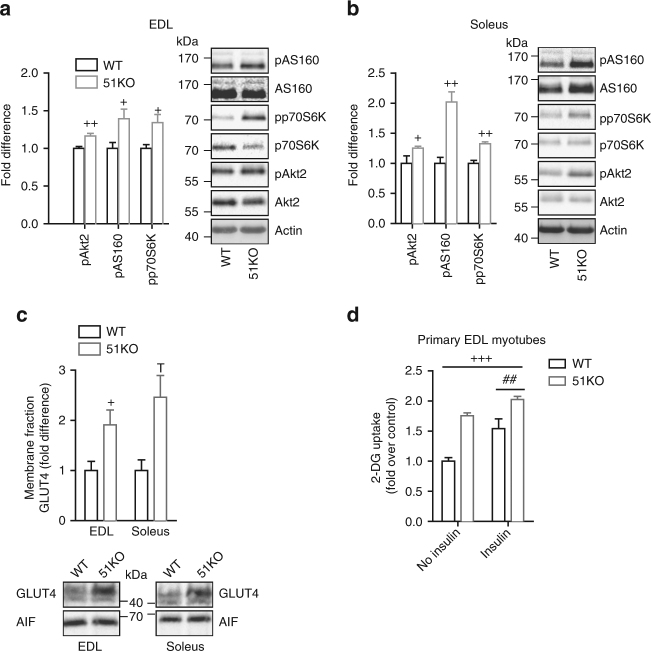
Fig. 4.
FKBP51 affects insulin signaling and consequently glucose uptake. a, b Insulin signaling was enhanced in EDL (a) and soleus (b) skeletal muscles of 51KO mice compared to WT mice as assessed by pAKT2, pAS160, and pp70S6K protein expression. c Following subcellular fractionation to isolate the plasma membrane compartment, we observed increased GLUT4 expression in skeletal muscle membrane fractions of 51KO mice. d In primary EDL myotubes, loss of FKBP51 heightened glucose uptake under both no insulin and insulin-stimulated states. For quantification of phosphorylated protein, n = 6 per group. For GLUT4 membrane localization, n = 3 per group. For glucose uptake experiments, 3 wells for each condition were measured. The data are expressed as relative fold change compared to wild-type condition ± SEM. + P < 0.05, ++ P < 0.01, +++ P < 0.001, ## P < 0.01, two-tailed t tests for a–d, two-way ANOVA for e; + significant genotype effect, # significant insulin effect, T trend for genotype. Supplementary Fig. 12 shows uncropped gel images