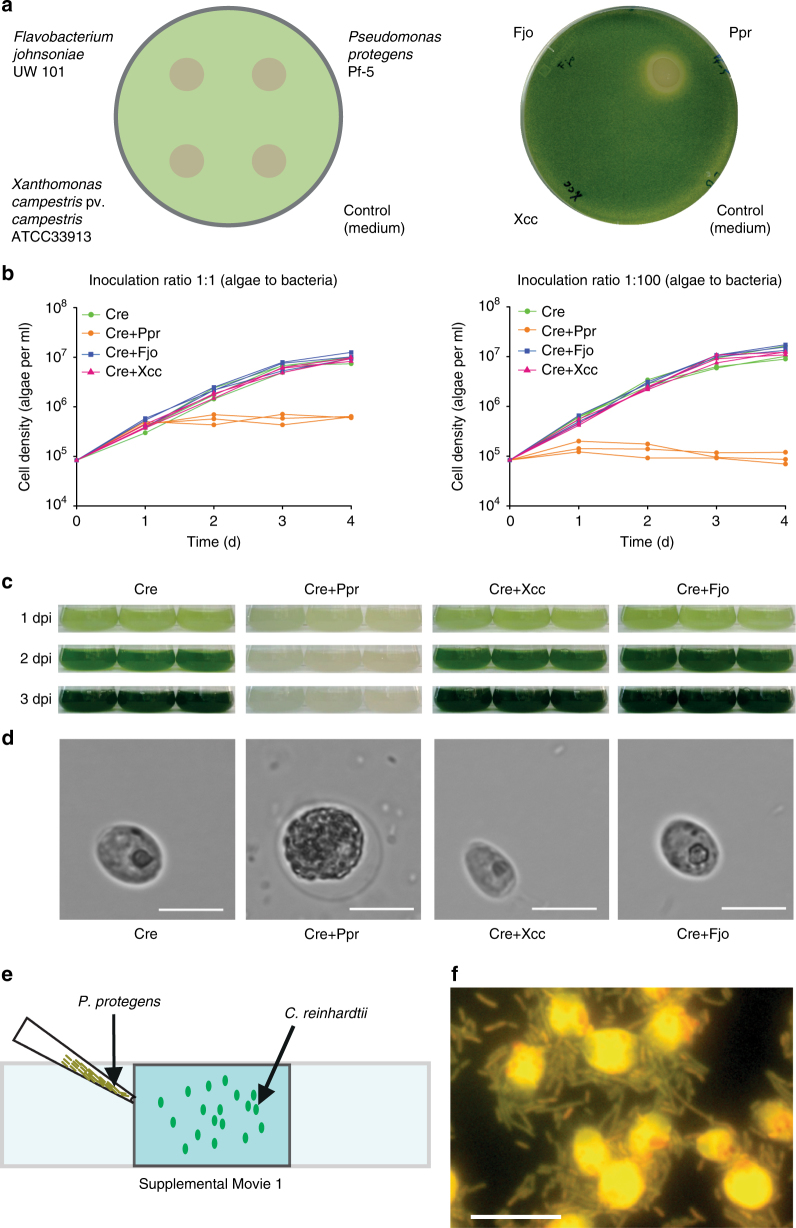
Fig. 1.
P. protegens swarms to C. reinhardtii and leads to growth arrest and changes in algal morphology. a Co-cultivation of C. reinhardtii and bacteria on agar plates after 3 days reveals the inhibitory effect of P. protegens. Suspensions of different bacteria were applied to restricted areas of a plate that contains C. reinhardtii within a top layer of TAP agar. LB medium was used as control. b Liquid co-cultivation at indicated ratios of algae to bacteria used for inoculation shows algal growth arrest in the presence of P. protegens. Cultures were inoculated to obtain initial cell densities of 8.3 × 104 algae per ml, and in coculture 8.3 × 104 (1:1) or 8.3 × 106 (1:100) bacteria per ml were added. Values of triplicate cultures are shown. c Photographs of the experiment depicted in b (1:100 ratio) show algal growth arrest by the color change. d Morphology change of algal cells in the presence of P. protegens after 24 h in mixed culture as compared to an axenic culture by bright-field microscopy using a magnification of ×630. Scale bar: 10 µm. e P. protegens swarms around the algal cells and surrounds them within minutes. Scheme depicting the experimental procedure used to visualize live interaction of P. protegens with C. reinhardtii (Supplementary Movie 1). Overall, 10 µl of an overnight culture of P. protegens in LB medium were introduced from one corner of the coverslip as shown in the scheme. f Cells of C. reinhardtii and P. protegens were immobilized after 10 min in coculture on a coated glass slide and stained with acridine orange. Cells were visualized using fluorescence microscopy at ×1000 magnification. Scale bar: 10 µm. Cre Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, Fjo Flavobacterium johnsoniae, Xcc Xanthomonas campestris pv. campestris, Ppr Pseudomonas protegens, dpi days post inoculation. a–e All experiments were performed in three biological replicates and representative pictures (d) and a representative Supplementary Movie 1 are shown. f shows a representative section of an acridine orange-stained sample as treated in e, but for 10 min. The experiments were replicated three (a) or two times (e) or performed once (b, d)