Figure 1.
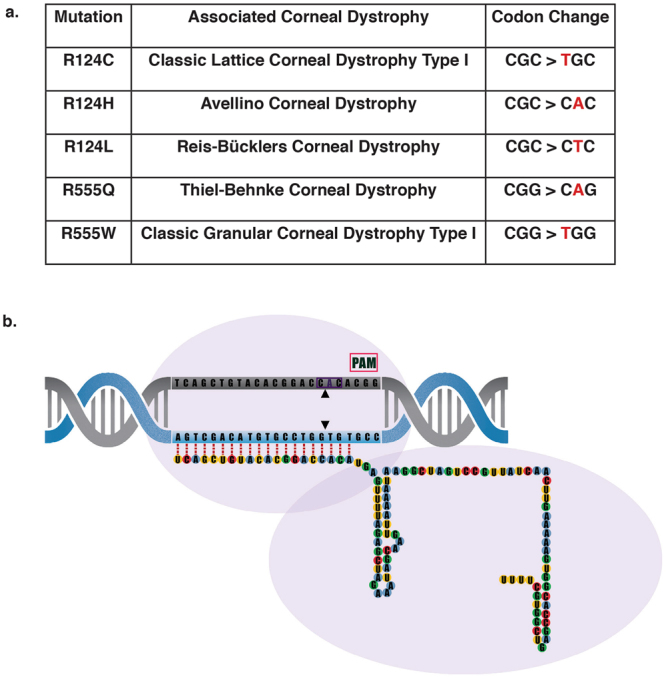
S. pyogenes Cas9 to treat dominant negative TGFBI corneal dystrophies. (a) Cas9 (purple outline) can be directed to cut any sequence in the genome (DNA target in grey), provided it is directly upstream of a protospacer adjacent motif known as PAM (pink box). This can be achieved by altering the 20 nucleotide guide sequence, which is associated with a 82 nucleotide scaffold. (b) 5 prevalent TGFBI mutations and their associated corneal dystrophy and codon change. (c) Schematic of the position of the 60 missense mutations across the TGFBI gene. The hotspots at exons 4, 11, 12 and 14 are evident, with exons 4 and 12 expanded to show the location of the 5 most prevalent TGFBI mutations; R124C, R124H, R125L, R555Q and R555W.
