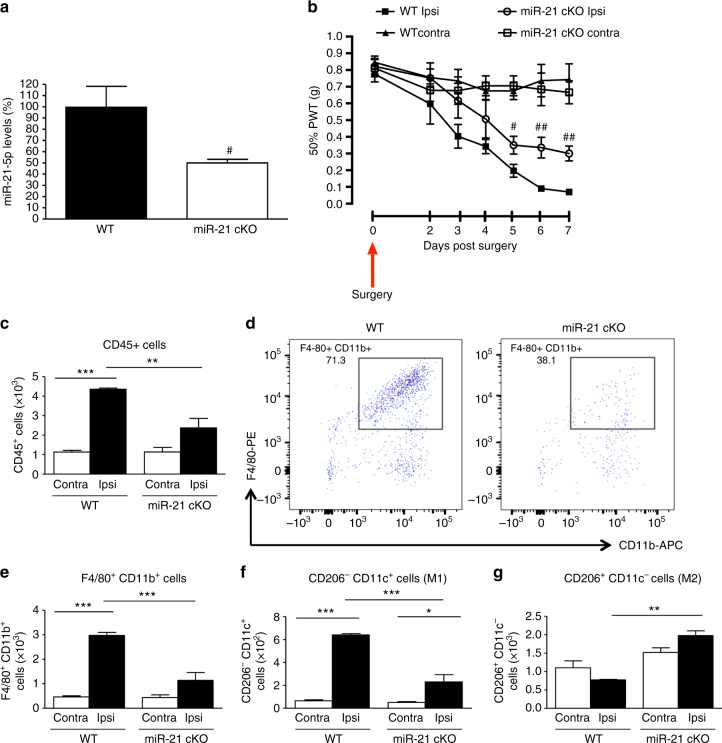
Fig. 10.
Conditional deletion of miR-21 in sensory neurons prevents the development of mechanical hypersensitivity and is associated with polarization of macrophages toward an anti-inflammatory phenotype. a Downregulation of miR-21-5p levels in DRG of miR-21 cKO compared to WT littermate mice. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.M., n = 5 mice for each group. # P < 0.05 compared to WT, Student’s t-test. b Effect of miR-21 deletion in DRG sensory neurons on the development of mechanical hypersensitivity following SNI. Data are presented as 50% of paw withdrawal thresholds (PWT); means ± S.E.M., n = 10 mice. # P < 0.05, ## P < 0.01, compared to WT ipsilateral, two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test. c Bar charts represent absolute number of leukocyte in DRG. d Representative scatterplots of immune cells sorted from pools of ipsilateral L4 and L5 DRG obtained from WT mice or miR-21 cKO mice, on day-7 post SNI injury. Numbers in gates refer to the percentage of positive cells for each specific marker. e Number of macrophages, f M1 macrophages (g) and M2 macrophages. Statistical analysis was performed on data from two independent experiments. Data are expressed as means ± S.E.M., n = 4 for each group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, one-way ANOVA, post hoc Bonferroni