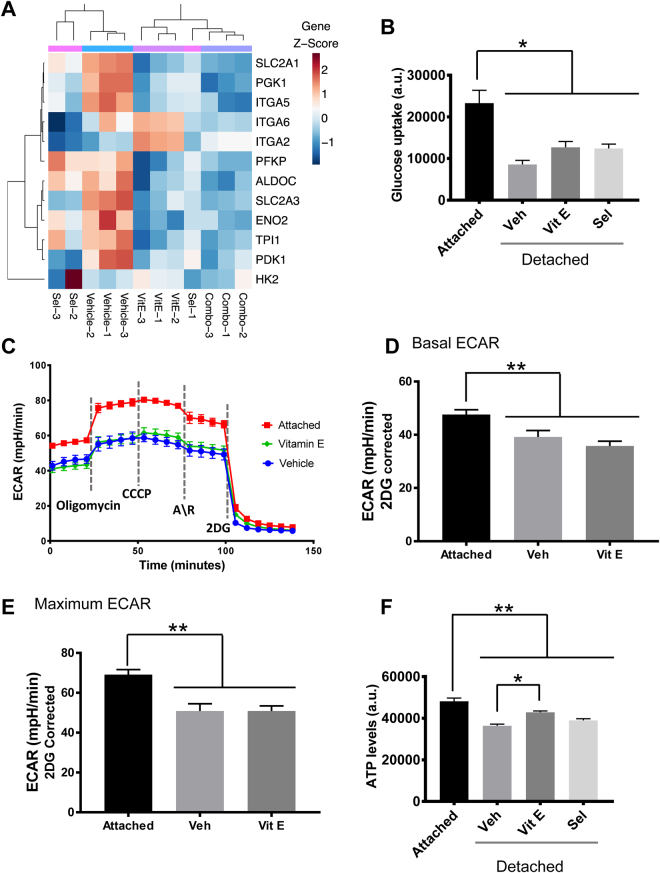
Figure 7.
Vitamin E promotes cell survival through a metabolic rescue of ECM detached cells. (A) Heatmap of differentially expressed genes in the glycolysis and cell attachment pathways identified to be affected by the gene set analysis showed a downregulation of both pathways to varying degrees by antioxidant treatment (B) Measurement of glucose uptake in adherent or non-adherent, (poly-HEMA coated plates), RWPE-1 cells showed a significant decrease in the detached cells that was not rescued by the antioxidants after 24 h. (C) ECAR analysis of RWPE-1 cells grown in adherent and non-adherent conditions and treated with the SELECT supplements for 24 h, n = 15. (D) Basal ECAR was calculated by subtracting non-glycolytic ECAR from the basal ECAR measurements vs vehicle. (E) Maximal ECAR was calculated by subtracting non-glycolytic ECAR from the ECAR measurements after the addition of oligomycin. (F) ATP levels measured in 24 h RWPE-1 cell cultures in adherent or non-adherent plates showed a significant ATP rescue by Vitamin E treatment, (n ≥ 3). Asterisks represent statistical significance (One way ANOVA with Tukey’s correction for multiple comparisons). *p ≤ 0.001, **p ≤ 0.0001; error bars represent SD. A.U. means arbitrary units.