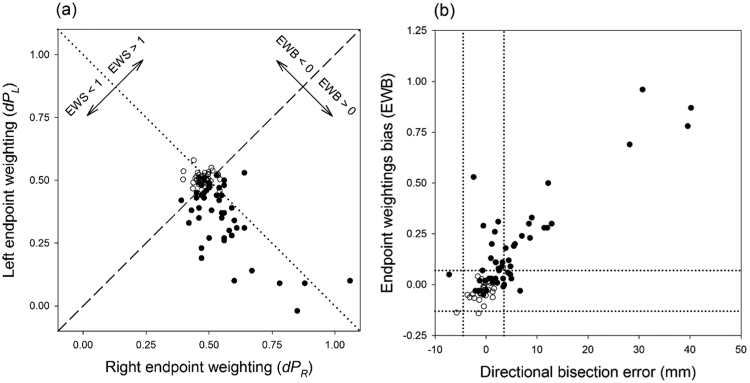
Fig. 2.
Experiment 1. (a) Scatterplot relating right and left endpoint weightings for 50 RBD patients (filled circles), and 30 healthy controls (open circles) (control data from McIntosh et al., 2005). The dashed diagonal represents the line on which the two endpoint weightings are equal, so that the endpoint weightings bias (EWB) equals zero. The dotted diagonal represents the line on which the endpoint weightings sum (EWS) equals one. (b) Scatterplot relating directional bisection error and endpoint weightings bias for participants in Fig. 2a. The dotted lines represent upper and lower cut-offs, for left and right neglect respectively, according to each measure (see Methods for details).