Figure 2.
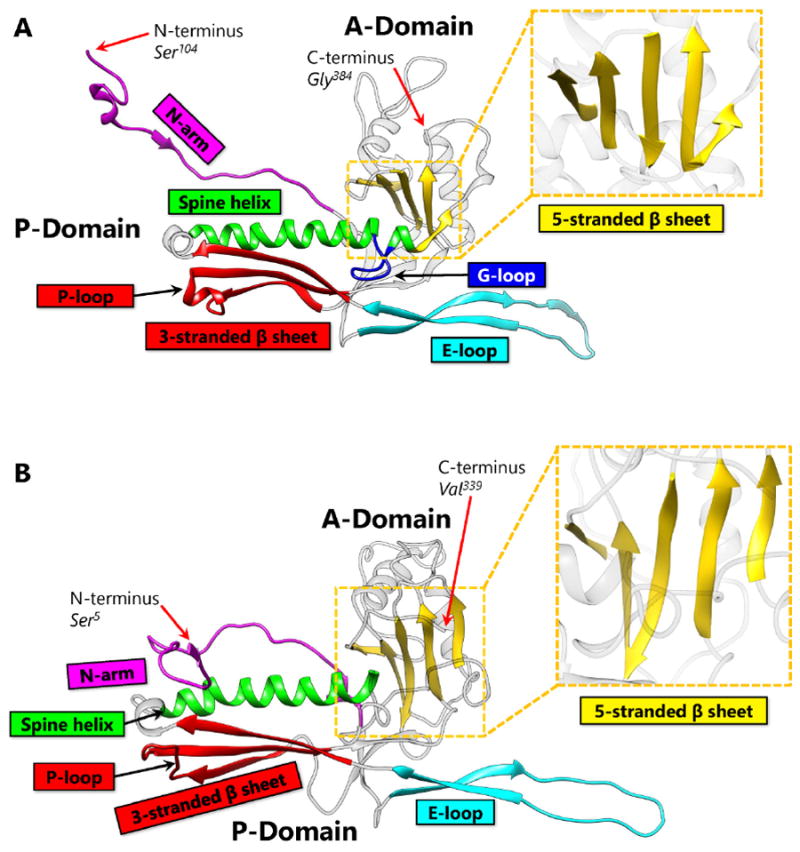
Capsid Protein Comparison Between HK97 and BPP-1. (A) The capsid protein of HK97, gp5 contains the HK97-like fold (Protein Data Bank [PDB] 2FT1). The capsid protein of HK97 is truncated during maturation and begins at Ser104, ending at Gly384. Major structural elements include the N terminal extension (N-arm, magenta), extended loop (E-loop, cyan), 3-stranded β sheet including the P-loop (red), spine α helix (Spine helix, green), glycine-rich loop (G-loop, blue), and 5-stranded β sheet (zoomed, yellow). Along with the 3-stranded β sheet, the spine helix with a G-loop interruption forms the P-domain. The 5-stranded β sheet forms the core of the A-domain and contains a ↑↑↓↑↑ sheet arrangement. The N-arm and the E-loop protrude from the core of the fold and are flexible to accommodate capsid curvature. (B) The capsid protein of BPP-1 (PDB 3J4U). Unlike gp5 of HK97, the capsid protein of BPP-1 is not truncated. It has the same color scheme as Figure 2A, and contains similar secondary structure elements. The N-arm of BPP-1 is curved such that the β strand can interact with the auxiliary protein (see Figure 5B).
