Figure 3.
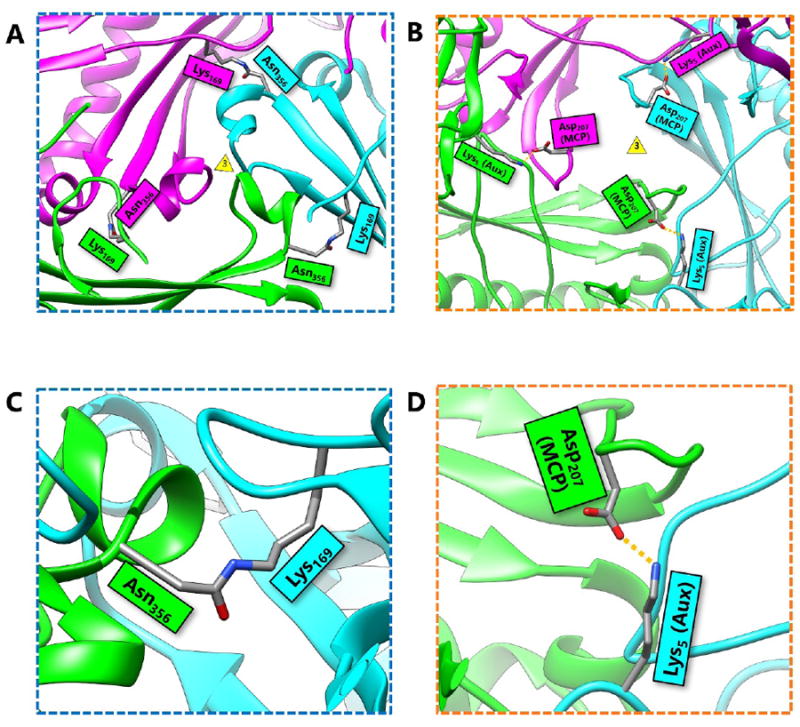
Comparison of HK97 Isopeptide Bonds and BPP-1 Salt Bridges at the 3-fold Axis. (A) A local three-fold interface of HK97 showing the location of isopeptide bonds. The three-fold vertex is indicated by the yellow triangle. Three isopeptide bonds crosslink hexamers and pentamers of the HK97 capsid. Additionally, the protein rings crisscross to form a network of covalently linked, concatenated protein rings, or a covalent chainmail. (B) A local three-fold interface of BPP-1 showing that BPP-1 has salt bridges, but no isopeptide bonds. The salt bridges form between charged residues of the MCP and the auxiliary protein (Aux). These salt bridges, combined with additional non-covalent interactions, complete the non-covalent chainmail of BPP-1. (C) Zoomed-in view of the HK97 isopeptide bond that forms between Lys169 and Asn356. It functions to chemically bind subunits of HK97 together without the use of additional proteins. (D) Zoomed-in view of the salt bridge in BPP-1 at the three-fold interface. It forms between the positively-charged residue Lys5 of the auxiliary protein and the negatively-charged residue Asp207 of the capsid protein.
