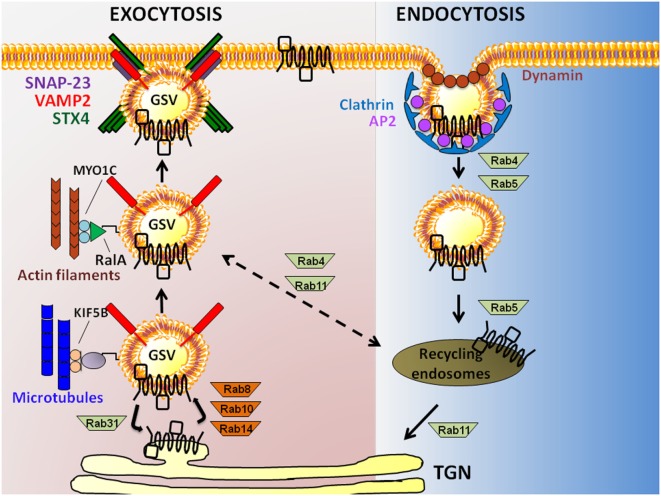
Figure 2.
Exocytosis to endocytosis, and back. Schematic model showing actin filament and microtubule-dependent exocytosis of glucose transporter-4 (GLUT4) (leftmost pathway), and clathrin-mediated GLUT4 endocytosis (rightmost pathway) in skeletal muscle and adipose cells. GLUT4 present at the plasma membrane (PM) is endocytosed in a Clathrin-dependent manner requiring the adaptor protein-2 (AP2) adapter and the GTPase Dynamin. Rab GTPases 4 and 5 are implicated in the distal step to generate recycling endosomes carrying GLUT4, afterwhich GLUT4 is taken to the trans-Golgi network (TGN) via Rab11 or possibly back to a GLUT4 storage vesicle (GSV) pool via Rab4/11. Exocytosis of GLUT4 in GSVs that also carry the vesicle SNARE [vesicle associated membrane protein-2 (VAMP2)] from the TGN requires Rabs8/10/14; Rab31 counteracts this action. GSVs travel along microtubules via kinesins (KIF5B) and actin filaments (via RalA and MYO1C), bringing GSVs into close proximity with the PM t-SNARE proteins [Syntaxin 4 (STX4) and synaptosomal-associated protein-23 (SNAP-23)].