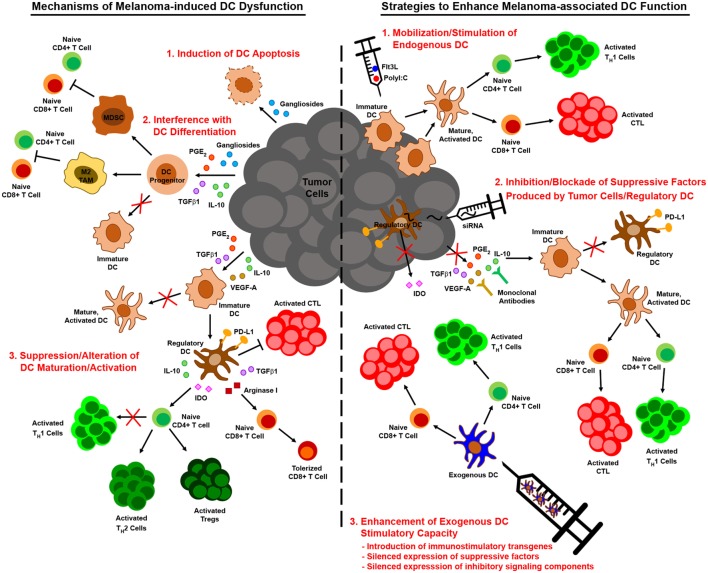
Figure 2.
Melanoma-associated dendritic cell (DC) dysfunction and therapeutic interventions to enhance DC-mediated anti-melanoma immune responses. Melanoma interferes with the function of DC by numerous mechanisms, including induction of DC apoptosis, blocking/altering DC development from hematopoietic precursors, suppressing DC maturation/activation, and driving the differentiation of tumor-promoting regulatory DC (left). Insights into these mechanisms of melanoma-altered DC dysfunction have informed strategies to augment DC-mediated anti-melanoma immune responses. These strategies include approaches that mobilize and stimulate endogenous DC, interventions that impede the production or action of immunosuppressive factors released by melanoma and associated cells in the tumor microenvironment, and regimens that employ exogenous DC that have been manipulated to resist suppressive elements and stimulate robust antitumor immunity (right).