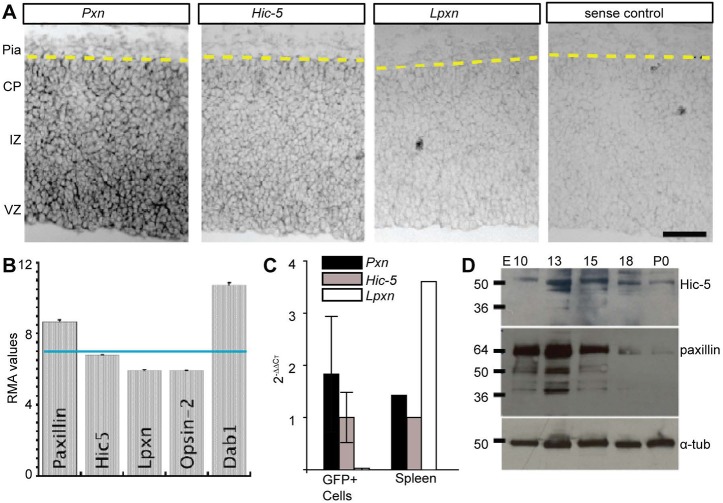
Fig. 1.
Paxillin and Hic-5 are expressed in the developing cortex. (A) In situ hybridization of E15.5 neocortex using paxillin (Pxn), Hic-5 and leupaxin (Lpxn) probes. Pxn and Hic-5 were detected prominently in the VZ, with lower in situ signal in the IZ and CP. (B) Microarray analysis of immature excitatory neurons isolated by FACS from Tg(Eomes-eGFP)Gsat cortex at E14.5 (Cameron et al., 2012). Pxn and Hic-5 RMA (robust multichip average) expression levels are above the expression level of Lpxn and eye-specific opsin 2 (not expressed). (C) RT-qPCR analysis of immature excitatory neurons (GFP+) isolated by FACS from Tg(Eomes-eGFP)Gsat cortex at E14.5 (n=3 embryos). Values were first normalized (to G6PDH) and then presented relative to Hic-5 2–ΔΔCT. Spleen tissue (n=1) was used as a positive control. (D) Western blot analyses of paxillin and Hic-5 protein in the developing cortex (E10-P0). Paxillin and Hic-5 are expressed highly during corticogenesis (E13-E15) but decrease perinatally (P0). α-tubulin was used as a loading control. VZ, ventricular zone; IZ, intermediate zone; CP, cortical plate. Scale bar: 50 µm.