Fig. 2.
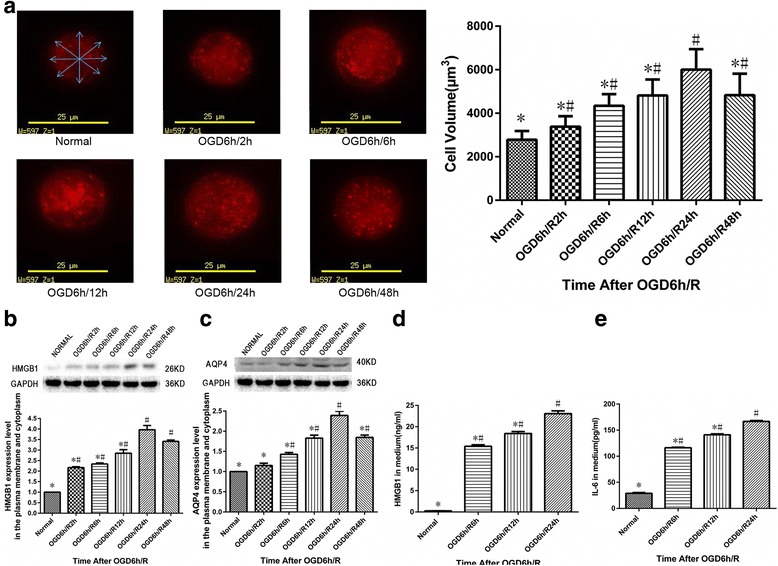
Effects of oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) on cellular swelling, high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1), and aquaporin-4 (AQP4) expression in cultured spinal cord astrocytes as well as levels of HMGB1 and interleukin-6 (IL-6) released into the surrounding medium. a Astrocyte volume measurement was performed using a Live Cell Imaging System. Cellular volume was calculated by the average value of four measured diameters of the largest compiled Z-slice image. Cellular volumes of spinal cord astrocytes were significantly increased at 2, 6, 12, 24, and 48 h during reoxygenation after OGD when compared with normal astrocytes. #P < 0.05 vs. normal group; *P < 0.05 vs. OGD6h/R24h group (three replicates). b Membrane and cytoplasmic HMGB1 expression was significantly increased in spinal cord astrocytes at different time points after OGD/R. #P < 0.05 vs. normal group; *P < 0.05 vs. OGD6h/R24h group (three replicates). c Membrane and cytoplasmic AQP4 expression was significantly increased in spinal cord astrocytes at different time points after OGD/R. #P < 0.05 vs. normal group; *P < 0.05 vs. OGD6h/R24h group (three replicates). d HMGB1 levels in the surrounding medium of spinal cord astrocytes were significantly increased at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD/R. #P < 0.05 vs. normal group; *P < 0.05 vs. OGD6h/R24h group (three replicates). e IL-6 levels in the surrounding medium of spinal cord astrocytes were significantly increased at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD/R. #P < 0.05 vs. normal group; *P < 0.05 vs. OGD6h/R24h group (three replicates)
