Fig. 4.
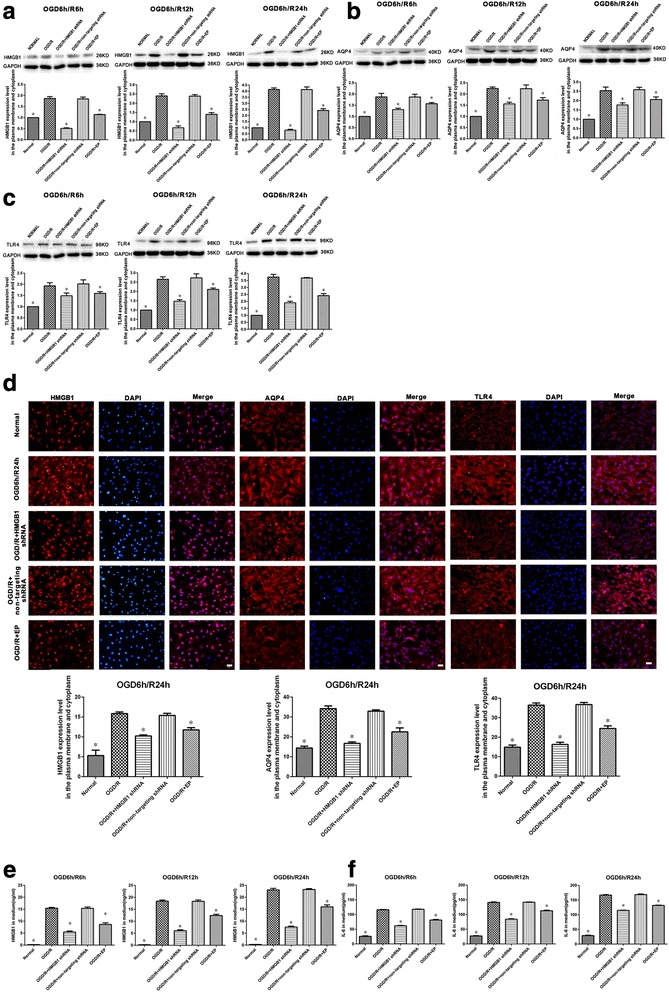
Effects of inhibiting high mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) on HMGB1, aquaporin-4 (AQP4), and toll-like receptor-4 (TLR4) expression in cultured spinal cord astrocytes after oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation (OGD/R) as well as levels of HMGB1 and interleukin-6 (IL-6) release into the surrounding medium. a Inhibiting HMGB1 using either HMGB1 shRNA or ethyl pyruvate (EP) significantly suppressed the increased levels of HMGB1 in both the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of spinal cord astrocytes at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD. *P < 0.05 vs. OGD/R group (three replicates). b Inhibiting HMGB1 significantly suppressed the increased levels of AQP4 in both the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of spinal cord astrocytes at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD. *P < 0.05 vs. OGD/R group (three replicates). c Inhibiting HMGB1 significantly suppressed increased levels of TLR4 in both the plasma membrane and cytoplasm of spinal cord astrocytes at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD. *P < 0.05 vs. OGD/R group (three replicates). d HMGB1, AQP4, and TLR4 immunofluorescence on spinal cord astrocytes at 24 h into the reoxygenation process after OGD showed significantly increased membrane and cytoplasmic levels of HMGB1, AQP4, and TLR4 in the OGD/R group when compared with those in the normal group. These were markedly suppressed in both the OGD/R + HMGB1 shRNA and OGD/R + EP groups (× 200, bar equal to 100 μm). *P < 0.05 vs. OGD/R group (three replicates). e, f Inhibiting HMGB1 mitigated increases in levels of HMGB1 and IL-6 in the surrounding medium when compared with levels in the OGD/R group at 6, 12, and 24 h during reoxygenation after OGD. *P < 0.05 vs. OGD/R group (three replicates)
