Figure 2. The microbiota induces epithelial NFIL3 expression through the circadian clock factor REV-ERBα and a DC-ILC3 signaling relay.
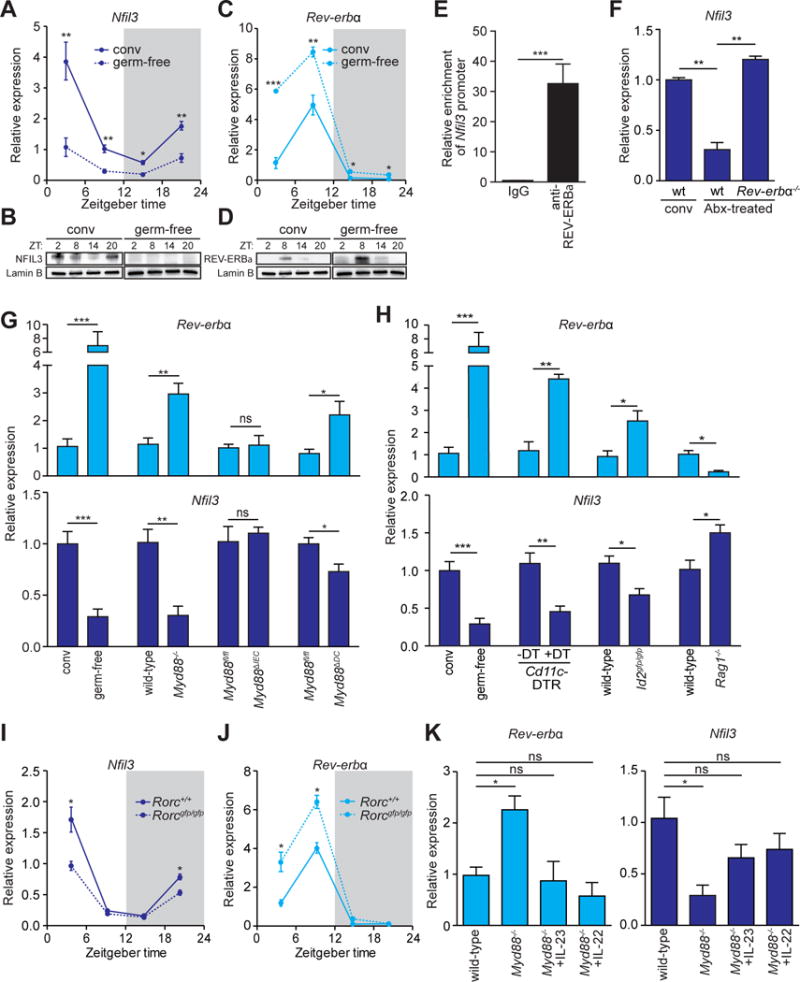
(A–D) qRT-PCR analysis of Nfil3 (A) and Rev-erbα (C) transcript abundance in small intestinal epithelial cells from germ-free (dotted line) and conventional mice (solid line) across a 24-hour day-night light cycle. Western blot analysis of NFIL3 (B) and REV-ERBα (D) was performed on small intestinal epithelial cells isolated from conventional or germ-free mice, Lamin B is the loading control. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitation assay on intestinal epithelial cells using immunoglobulin G (IgG) or anti-REV-ERBα antibody. Precipitated fragments of the Nfil3 promoter were detected by qRT-PCR. (F) qRT-PCR analysis of epithelial Nfil3 expression in conventional wild-type, antibiotic (Abx)-treated wild-type or Abx-treated Rev-erbα−/− mice. (G) qRT-PCR analysis of epithelial Rev-erbα and Nfil3 expression in germ-free and conventional wild-type mice and conventional Myd88fl/fl, Myd88−/−, Myd88ΔIEC (epithelial cell-specific knockout) and Myd88ΔDC (DC-specific knockout) mice. (H) qRT-PCR analysis of epithelial Rev-erbα and Nfil3 expression in germ-free and conventional wild-type mice, conventional Cd11c-DTR mice that were untreated or treated with Diphtheria toxin (DT), Id2gfp/gfp and Rag1−/− mice. (I,J) qRT-PCR analysis of epithelial Nfil3 (I) and Rev-erbα (J) expression in Rorc+/+ (solid line) and Rorcgfp/gfp (dotted line) mice. (K) qRT-PCR analysis of epithelial Rev-erbα and Nfil3 expression in Myd88−/− mice treated with recombinant IL-23, IL-22 or vehicle. Data in E,F,G,H, and K were collected at ZT4. N=3–8 mice per group. Means±SEM are plotted; statistics were performed with Student’s t-test or one-way ANOVA. *p<0.05; **p<0.01; ***p<0.001; ns, not significant; conv, conventional; ZT, Zeitgeber time.
