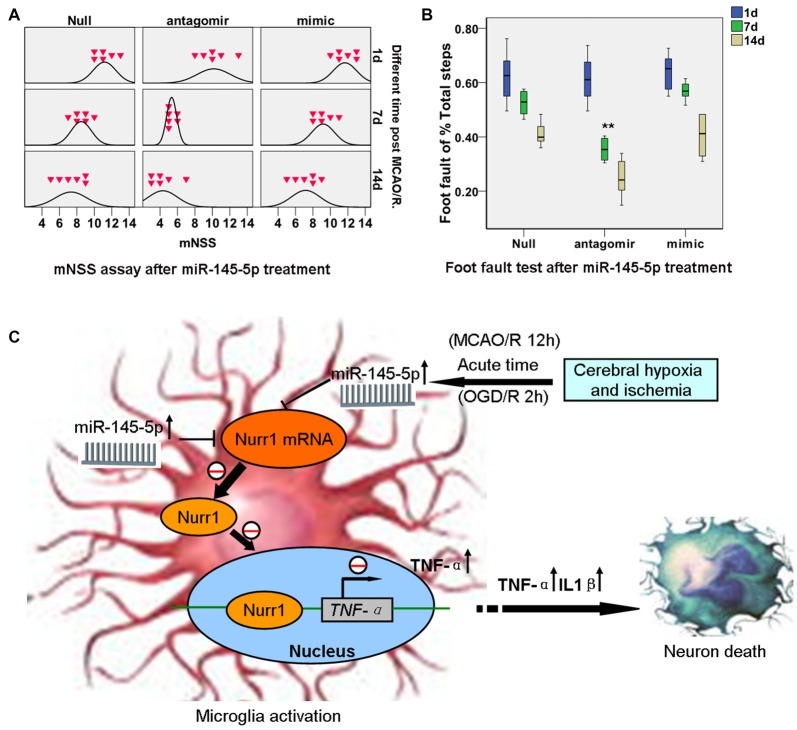
Figure 7.
miR-145-5p interruption facilitates neurological outcome of rats post MCAO/R. Modified Neurological Severity Score (mNSS) and foot fault tests were assessed on days 1, 7 and 14 after MCAO/R. (A) mNSS in antago-miR-145-5p animals were significantly decreased at both 7d and 14d after MCAO/R (p < 0.05). (B) Foot fault test, for the front left and hind left limbs were significantly lower in antagomiR-145-5p animals than that of miR-145-5p mimic and null animals. n = 54 for the combination group. (C) The graphical summary. Here, we describe a novel miR-145-5p regulatory mechanism of Nurr1 that can act downstream of TNF-α activation. In acute cerebral ischemia (MCAO/R 12 h) of rats and OGD/R 2 h of microglia, Nurr1 inhibits TNF-α expression by binding promoter of TNF-α gene. This regulatory effect is inhibited by Nurr1 protein decline that induced by miR-145-5p overexpression. Blocking the abnormal activation of miR-145-5p-Nurr1-TNF-α axis signaling can relieve neurons death upon MCAO/R of rats in acute time. **p < 0.01.