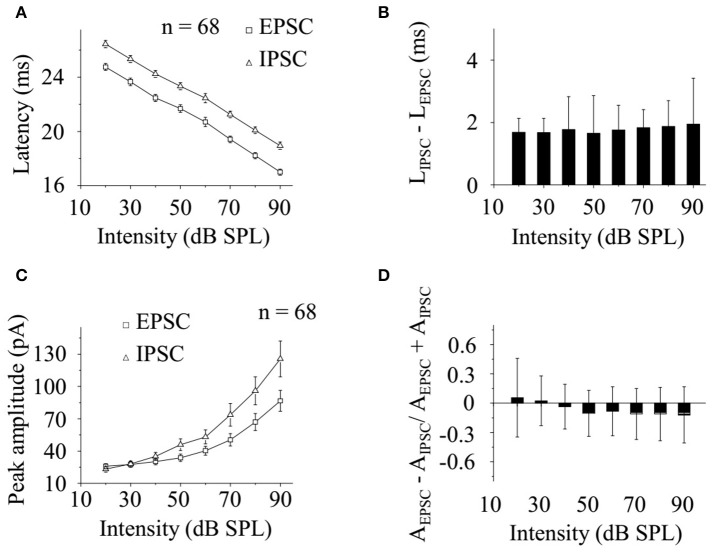
Figure 5.
CA3 neurons received balanced excitatory and inhibitory inputs evoked by broadband noise in awake animals. (A) The latencies of EPSC (square) and IPSC (triangle) evoked by broadband noise on recorded CA3 neurons (n = 68) changed linearly along with the sound levels. (B) The difference between the latencies of EPSC and IPSC (LIPSC–LEPSC) were similar at different sound intensities [One-way ANOVA, between groups (combined): P = 0.785; LSD's Tests for multiple comparisons. All P > 0.05]. (C) The peak amplitudes of noise-evoked EPSC (square) and IPSC (triangle) changed exponentially as a function of sound intensity. (D) The normalized peak amplitude difference between EPSC and IPSC at different sound intensities (AEPSC − AIPSC/AEPSC + AIPSC) had no substantial differences [One-way ANOVA, between groups (combined): P = 0.073; LSD's Tests for multiple comparisons. P > 0.05 with a few exceptions: P = 0.014 (20–80 dB), 0.022 (30–80 dB), 0.023 (40–80 dB), 0.037 (60–80 dB), 0.024 (20–90 dB), 0.032 (30–90 dB), 0.034 (40–90 dB), 0.045 (60–90dB)].