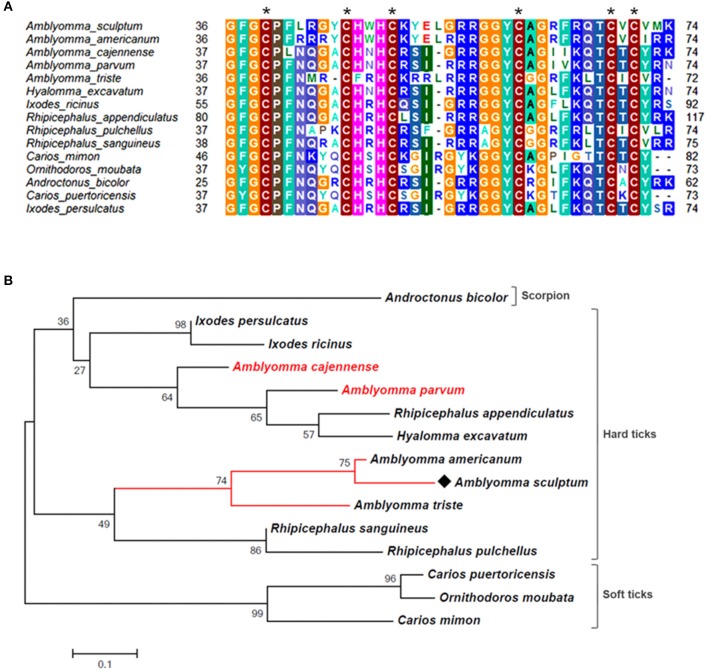
Figure 5.
MSA and phylogenetic analysis of defensins. (A) Multiple sequence alignment of protein sequences was performed using MUSCLE method. The numbers flanking the alignment represent the start (left) and end (right) amino acid position of each sequence in the protein domain. Asterisks highlight the conserved cysteine residues. Threshold for shading colors of amino acid similarity was 50%. (B) A phylogenetic tree was constructed with protein sequences from ticks and scorpion using Maximum Likelihood (ML) method. Numbers next to the branches represent the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together in the bootstrap test (1,000 replicates). The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths measured in the number of substitutions per site. The analysis involved 15 amino acid sequences (accession numbers available in Supplementary Table 2). All positions containing gaps and missing data were eliminated. There were a total of 58 positions in the final dataset. Bar scale at the bottom indicates 10% amino acid divergence. Diamond symbol refers to the CDS Acaj-65746 from the sialotranscriptome of A. scultpum identified in this work.