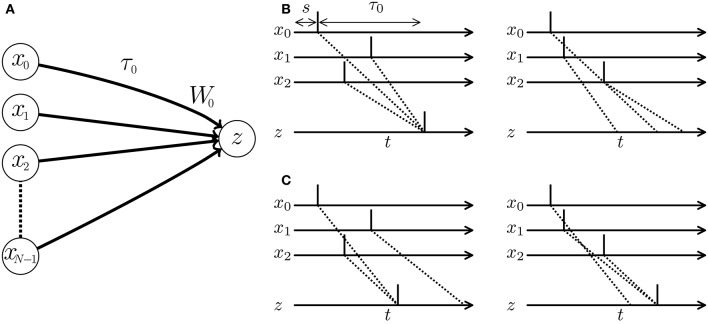
Figure 1.
(A) Schematic of a spiking neural network (SNN) consisting of multiple pre-synaptic neurons xi and a post-synaptic neuron z. W0 denotes the weight of the synapse projecting from the pre-synaptic neuron x0 to the post-synaptic neuron z, and τ0 denotes the conduction delay of the axon corresponding to the synapse. (B,C) Post-synaptic spikes in response to spatio-temporal spike patterns. Each vertical line denotes a spike elicited by a neuron. Dotted lines show the transmission paths of the pre-synaptic spikes to the post-synaptic neuron z. (B) When the conduction delays are fixed, the post-synaptic neuron responds to the spatio-temporal pattern of pre-synaptic spikes and elicits a spike (left panel), but is unresponsive to a second pattern (right panel). (C) When the conduction delays are plastic, the optimized SNN generates post-synaptic spikes at times depending on the given spatio-temporal patterns of the pre-synaptic spikes.