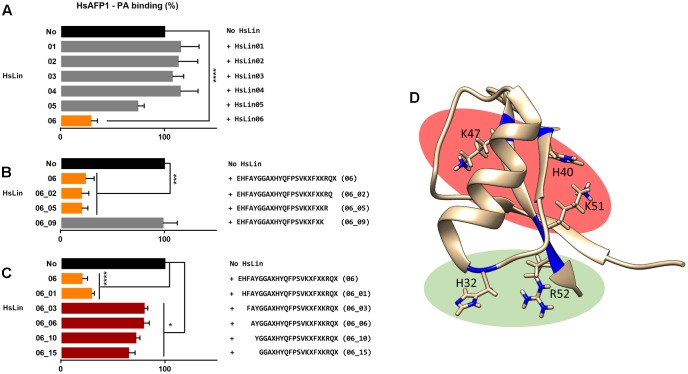
FIGURE 3.
Amino acids of HsAFP1 important for phosphatidic acid (PA) binding, using competitive rELISA assays. Competition of 12.5 μM HsAFP1 with 50 μM HsLin01-06 (A), C-truncated HsLin06 variants (HsLin06_02;05;09 in Figure 2; (B) or N-truncated variants (HsLin06_01;03;06;10;15 in Figure 2; (C) with both peptides co-incubated. Data are means ± SEM, for n ≥ 3 experiments. Data are expressed relative to the HsAFP1-PA binding without HsLin. Significant differences between HsAFP1 and HsAFP1 + 4x HsLin interactions were determined via one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett multiple comparison, with ∗, ∗∗∗, and ∗∗∗∗ representing P < 0.05, P < 0.001, and P < 0.0001, respectively. (D) 3D structure of HsAFP1 with the positively charged amino acids [histidine (H) 32 and 40, lysine (K) 47, K51 and arginine (R) 52] of HsLin06 drawn in blue on its backbone, using the Chimera visualization program. Green clustered amino acids (H32 and R52) are important for PA binding while the red clustered (H40, K47 and K51) are not.