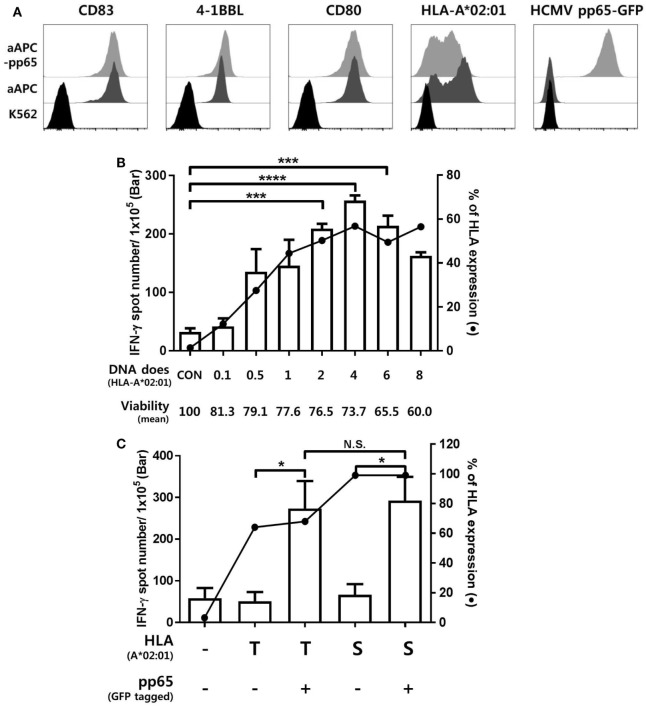
Figure 1.
Establishment of an artificial antigen-presenting cell (aAPC) system to detect cytomegalovirus (CMV) pp65-specific CD8+ T cell responses restricted by a single human leukocyte antigen (HLA) class I allotype. (A) Establishment of aAPCs expressing CD83, 4-1BBL, and CD80, and aAPC-pp65 expressing CMV pp65 from the K562 cell line. To detect the CD8+ T cell response to CMV pp65, aAPC-pp65 were transfected with HLA-A*02:01 plasmid DNA. The expression of transferred genes was assessed by flow cytometry. (B) Optimization of HLA class I gene transfection to detect CD8+ T cell responses. HLA-A*0201 plasmid DNA concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 8 µg were used for transfection in 1 × 106 aAPC-pp65. CD8+ T cells showing strong responses to pp65 (HD01) were cocultured with aAPC-pp65 for the interferon-γ (IFN-γ) enzyme-linked immunospot (ELISPOT) assay. (C) Comparison of transient transfection with 4 µg of plasmid DNA (T) and stable expression with lentivirus vector (S) of HLA-A*02:01 in stimulating CD8+ T cells. CD8+ T cells (HD01) were cocultured with aAPC (−) and aAPC-pp65 (+) for IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. Results represent the mean percentage of expression from three independent experiments with SD (bars). P values were calculated by 1-way ANOVA (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001; N.S., not significant).