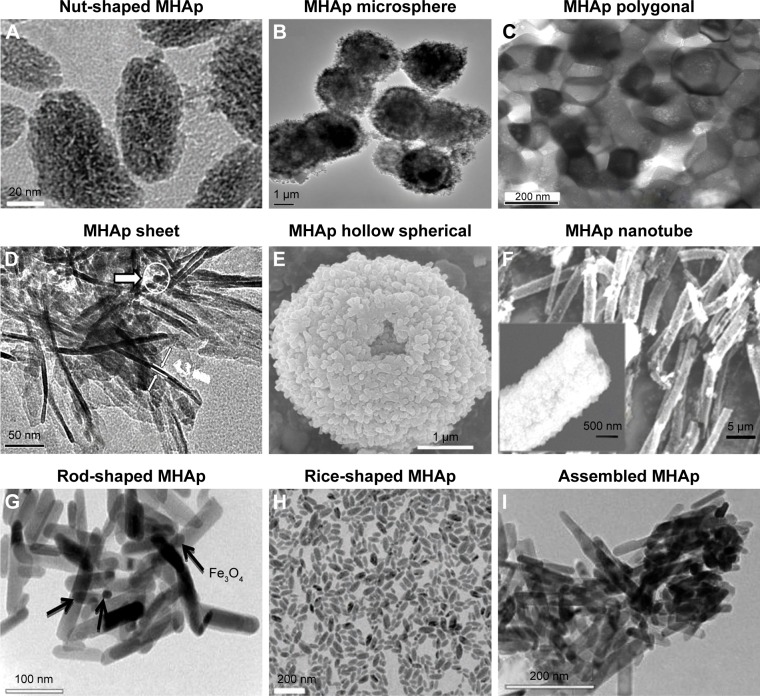
Figure 2.
MHAp structure synthesized in different shapes (A–H). (A) Reproduced from Cui X, Green MA, Blower PJ, et al. Al(OH)3 facilitated synthesis of water-soluble, magnetic, radiolabelled and fluorescent hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb). 2015;51(45):9332–9335 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.88 (B) Reproduced from Lin K, Chen L, Liu P, et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH-responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm. 2013;15(15):2999–3008 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.89 (C) Reprinted with permission from Boda SK, Anupama AV, Basu B, Sahoo B. Structural and magnetic phase transformations of hydroxyapatite magnetite composites under inert and ambient sintering atmospheres. J Phys Chem C. 2015;119(2):6539–6555. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society.90 (D) Reproduced from Chen F, Li C, Zhu YJ, Zhao XY, Lu BQ, Wu J. Magnetic nanocomposite of hydroxyapatite ultrathin nanosheets/Fe3O4 nanoparticles: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis and application in pH-responsive drug release. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(10):1074–1081 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.78 (E) Reproduced from Lin K, Chen L, Liu P, et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH-responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm. 2013;15(15):2999–3008 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.89 (F) Reprinted from Singh RK, El-Fiqi AM, Patel KD, Kim HW. A novel preparation of magnetic hydroxyapatite nanotubes. Mater Lett. 2012;75:130–133. Copyright 2012, with permission from Elsevier.79 (G) Reproduced from Bharath G, Prabhu D, Mangalaraj D, Viswanathan C, Ponpandian N. Facile in situ growth of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on hydroxyapatite nanorods for pH dependent adsorption and controlled release of proteins. RSC Adv. 2014;4(92):50510–50520 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.77 (H) Reproduced from Cui X, Green MA, Blower PJ, et al. Al(OH)3 facilitated synthesis of water-soluble, magnetic, radiolabelled and fluorescent hydroxyapatite nanoparticles. Chem Commun (Camb). 2015;51(45):9332–9335 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.88 (I) Reproduced from Bharath G, Prabhu D, Mangalaraj D, Viswanathan C, Ponpandian N. Facile in situ growth of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on hydroxyapatite nanorods for pH dependent adsorption and controlled release of proteins. RSC Adv. 2014;4(92):50510–50520 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.77
Abbreviation: MHAp, magnetic hydroxyapatite.