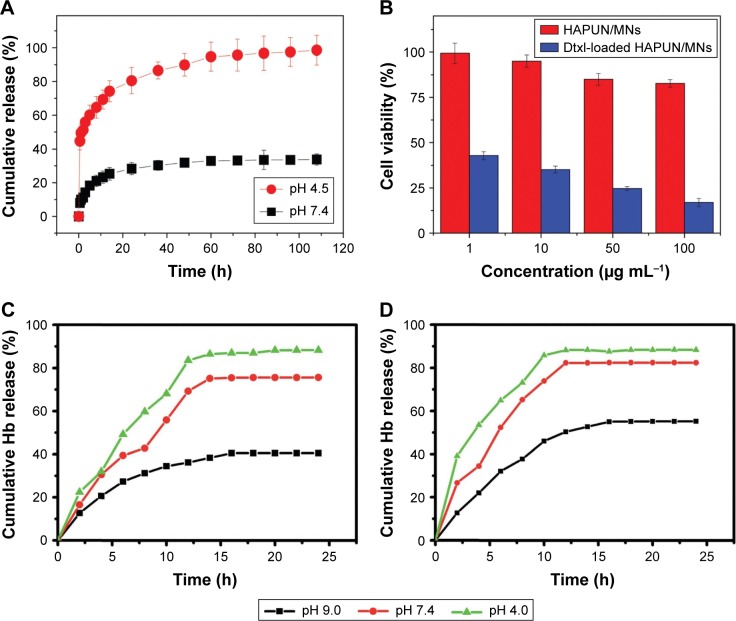
Figure 7.
Drug and protein release kinetics of different MHAp nanostructures at different pH conditions. (A) The cumulative drug release percentages of docetaxel from the HAPUN/MNs nanocomposite drug delivery system in PBS with different pH values of 7.4 and 4.5. Reproduced from Chen F, Li C, Zhu YJ, Zhao XY, Lu BQ, Wu J. Magnetic nanocomposite of hydroxyapatite ultrathin nanosheets/Fe3O4 nanoparticles: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis and application in pH-responsive drug release. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(10):1074–1081 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.78 (B) Cell viability tests of the HAPUN/MNs without and with docetaxel drug loading. Reproduced from Chen F, Li C, Zhu YJ, Zhao XY, Lu BQ, Wu J. Magnetic nanocomposite of hydroxyapatite ultrathin nanosheets/Fe3O4 nanoparticles: microwave-assisted rapid synthesis and application in pH-responsive drug release. Biomater Sci. 2013;1(10):1074–1081 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.78 Cumulative release of hemoglobin loaded on (C) Fe3O4/HAp-1 and (D) Fe3O4/HAp-2 nanocomposites at different initial pH values of 7.4 and 9.0 in PBS at room temperature. Reproduced from Bharath G, Prabhu D, Mangalaraj D, Viswanathan C, Ponpandian N. Facile in situ growth of Fe3O4 nanoparticles on hydroxyapatite nanorods for pH dependent adsorption and controlled release of proteins. RSC Adv. 2014;4(92):50510–50520 with permission of The Royal Society of Chemistry.77
Abbreviations: MHAp, magnetic hydroxyapatite; PBS, phosphate buffer solution; HAp, hydroxyapatite; Hb, hemoglobin; Dtxl, docetaxel; HAPUN/MN, HAp ultrathin nanosheet.