Figure 1.
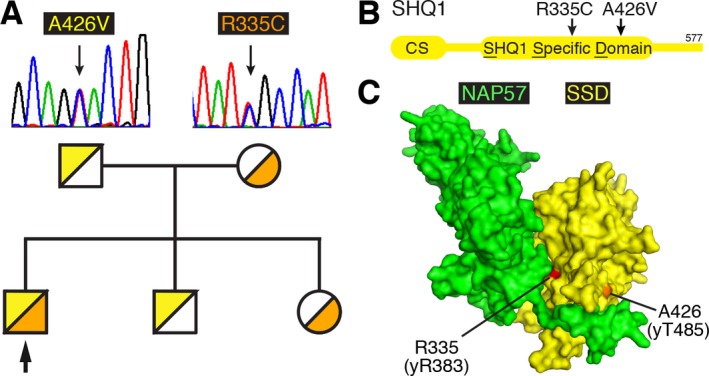
Pedigree and location of SHQ1 mutations. (A) Sanger sequencing of the father and mother confirms the hemizygous mutations of p.A426V (c.1277C>T) and p.R335C (c.1003C>T) respectively (NM_018130.2). The pedigree of the family is indicated below with the proband pinpointed by an arrow. (B) Schematic of the SHQ1 protein sequence with the N‐terminal CS and the central SHQ1 specific domain (SSD) that harbors the mutations. (C) Location of the equivalent positions mapped onto the structure of the yeast SSD – NAP57 (Cbf5p) complex (PDB ID: 3uai).
