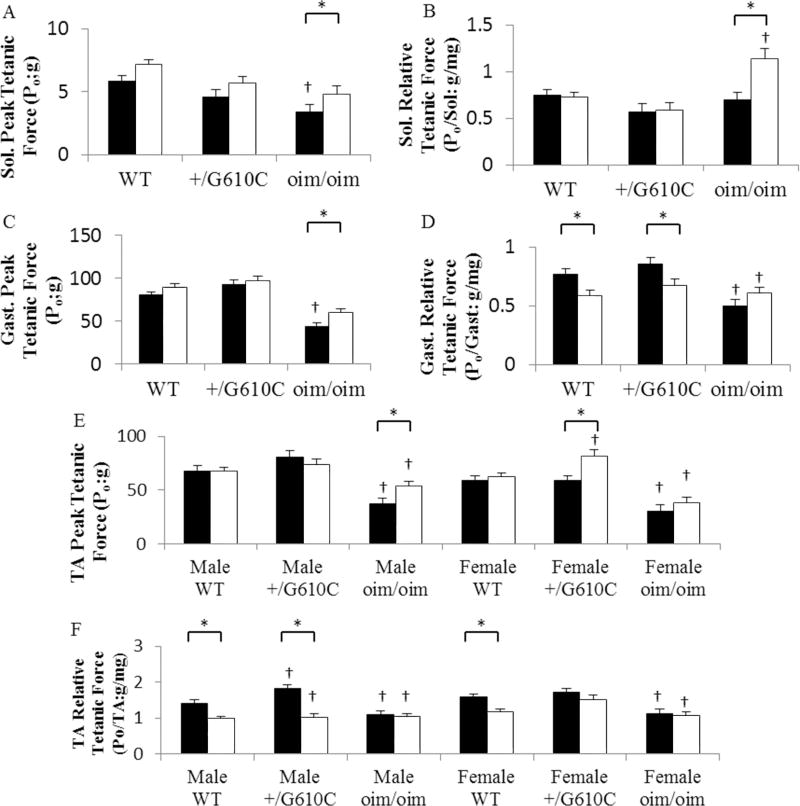
Figure 5.
oim/oim mice had reduced absolute and relative peak tetanic force (Po) as compared to WT and +/G610C counterparts (A–F). sActRIIB-mFc treated oim/oim mice exhibited increased peak Po as compared vehicle treated counterparts (A, C and E). sActRIIB-mFc treated WT and +/G610C mice exhibited reduced relative peak tetanic force as compared to vehicle treated counterparts (B, D, and F). (A) Sol. Peak tetanic force (Po), (B) Sol. relative Po, (C) Gast Peak Po, (D) Gast. Relative Po, (E) TA Peak Po, and (F) TA relative Po of 4 months old WT, +/G610C, and oim/oim vehicle (solid bars: control) and sActRIIB-mFc (open bars) treated mice. (n=10–30 per groups; TA Peak Po n=6–16 per groups). The genotype main effect was evaluated. Gast and Sol values are the LSmeans±SE of the combined genotype values regardless of sex, and the TA exhibited a genotype × sex interaction, and the values are LSmeans±SE separated by sex and genotype. *p<0.05; †p<0.05 vs. WT+vehicle treated mice.