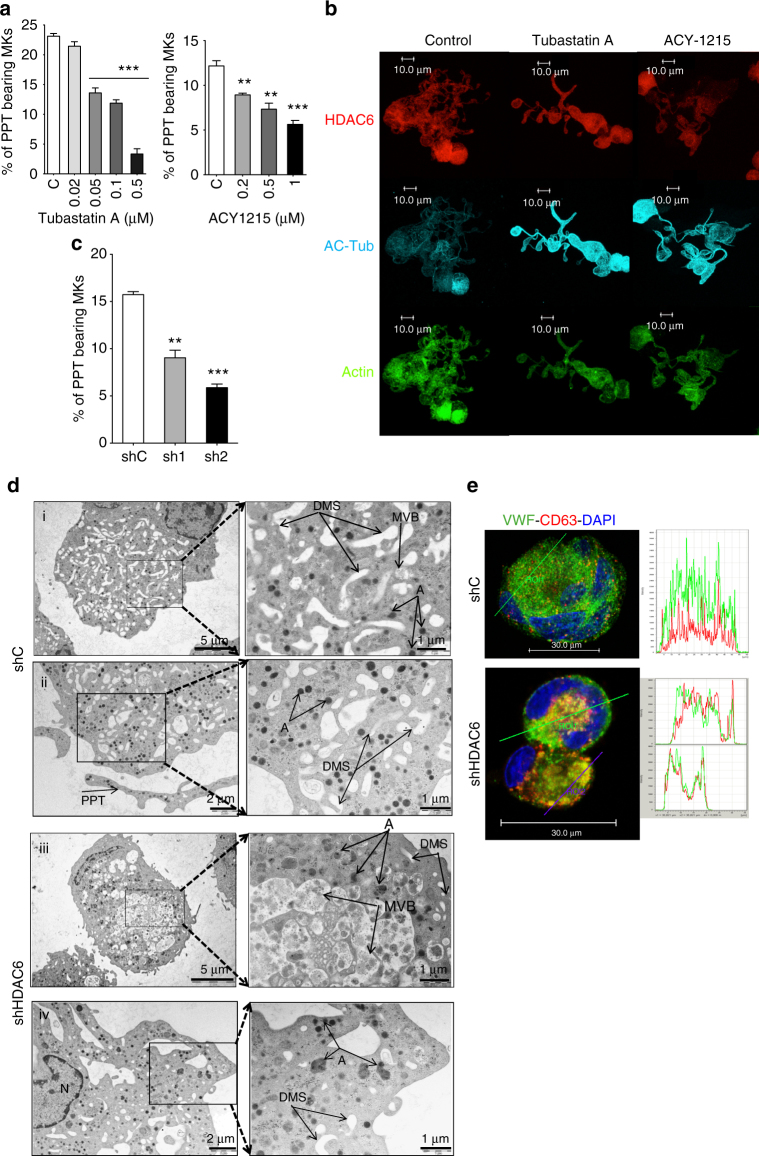
Fig. 3.
Effects of a pharmaceutical and a genetic inhibition of HDAC6 on terminal human MK differentiation. a ACY1215 and Tubastatin A decreases PPF. b Confocal analysis of untreated and treated MKs. Proplatelets derived from treated MKs display shorter extensions compared to untreated MKs. Bar represent 10 µm. c sh1 and sh2 leads to a specific inhibition of PPF. Results are representative of three independent experiments (n = 3). Unpaired Student’s t test:**p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001. d Ultrastructure analysis of shC and shHDAC6 MKs by transmission electron microscopy. (i, ii) Two MKs with a normal ultrastructure in the sh control with an enlargement, a regular development and distribution of demarcation membrane system (DMS), α-granules (a) and multivesicular bodies (MVB). We can also observe normal proplatelet (PPT) produced in vitro. (iii, iv) Two examples of abnormal ultrastructure of shHDAC6-treated MKs. Enlargement on both shHDAC6 MKs reveal either (iii) an abnormal presence of cytoplasmic vacuoles containing numerous microvesicles looking to large MVB and giant α-granules, or (iv) mature MKs displaying an heterogeneous granules size content. e Confocal analysis of CD63 and vWF in MKs transduced with shC or with shHDAC6. Bar represent 30 µm. Error bars are SEM