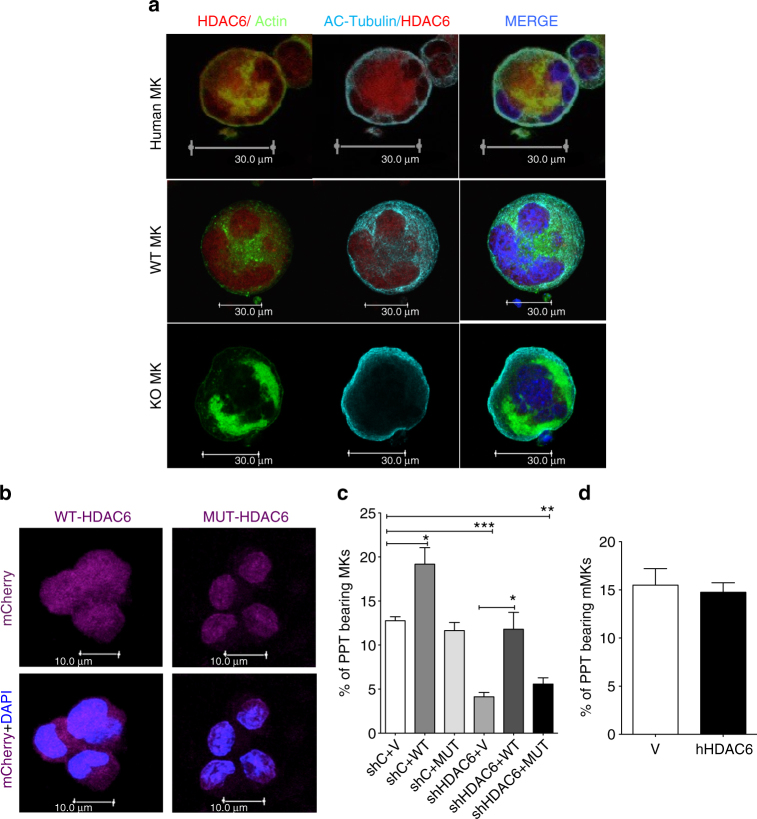
Fig. 5.
Differential HDAC6 localization in human and murine MKs does not explain the different phenotypes. a Immunofluoresence analysis showing localization of mHDAC6 and hHDAC6 in MKs. b Immunofluorescence analysis showing cytoplasmic WT-HDAC6 and nuclear MUT-HDAC6 accumulation in human MKs. c WT-HDAC6 but not MUT-HDAC6 reversed the shHDAC6-induced PPF decrease in human MKs. hMKs were either cotransduced provide space with sh Control (shC) with our without an empty vector (V) or WT-HDAC6 (cytoplamic) or NES-muted HDAC6 (nuclear, MUT) or cotransduced with shHDAC6 with or without an empty vector or WT-HDAC6 or MUT-HDAC6. d Cytoplasmic HDAC6 is not required for murine PPF in vitro. mMKs were transduced with either empty vector (V) or human WT-HDAC6 (hHDAC6, cytoplasmic) and allowed to form PPTs in vitro. Results are representative of three independent experiments. Unpaired Student’s t test, *p < 0.05; **p < 0.001; ***p < 0.0001. Error bars are SEM