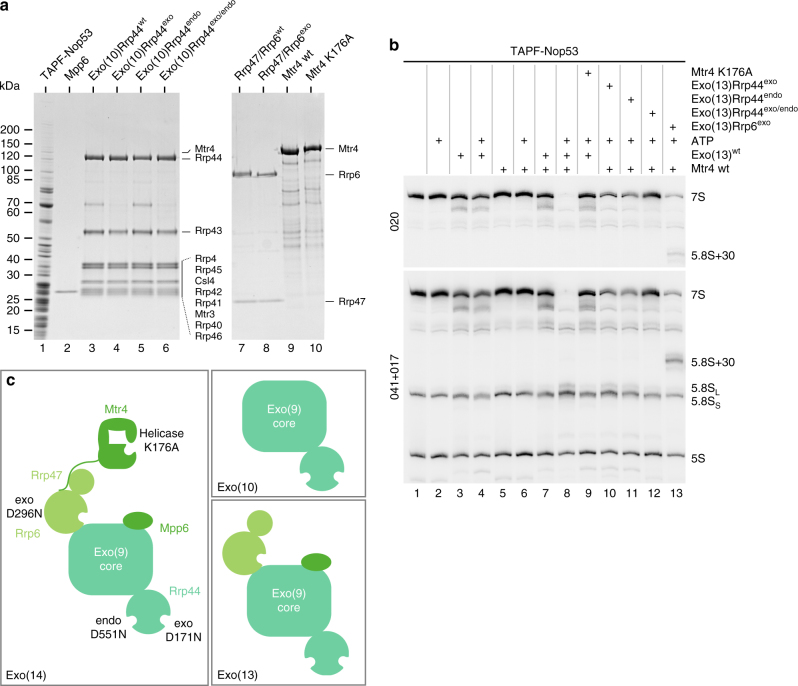
Fig. 2.
In vitro assay for 7S→5.8S pre-rRNA processing in purified pre-60S particles catalysed by the recombinant nuclear exosome and cofactors. a SDS-PAGE and Coomassie staining of the protein samples used for in vitro 7S→5.8S pre-rRNA processing. Pre-60S particles containing 7S substrate pre-rRNA were affinity-purified via TAPF-Nop53. All the yeast exosome subunits and Mtr4 were expressed recombinantly in E. coli and subsequently purified from cell lysates. Exo(10) comprises the exosome core and includes Rrp44, either in wt or catalytic mutant form, Exo(10)Rrp44exo, Exo(10)Rrp44endo, Exo(10)Rrp44exo/endo, Rrp47 and Rrp6, in mutant and wt form, the latter added as a dimer, and Mpp6 alone. Together, they form Exo(13), which corresponds to the endogenous exosome purified via Rrp6-FTpA. b Northern blot for the detection of 7S pre-rRNA, 5.8S rRNA and 5S rRNA species after the in vitro processing reaction. Processing of 7S pre-rRNA from pre-60S particles (TAPF-Nop53) using the recombinantly purified exosome (Exo(13)) in wt and mutant forms and its cofactor Mtr4, either wt or K176A mutant, in the presence or absence of ATP. 7S pre-rRNA was detected with two different probes. 5S rRNA served as a loading control. c Schematic representation of the different exosome modules/complexes—Exo(10), Exo(13) and Exo(14)—assembled using recombinant proteins, used in the various in vitro processing assays. Exo(14) also contains the Mtr4 helicase. Further depicted are the enzymatically active subunits of the exosome with their catalytic centres (exonuclease, endonuclease, ATPase) and the mutations generated at these sites