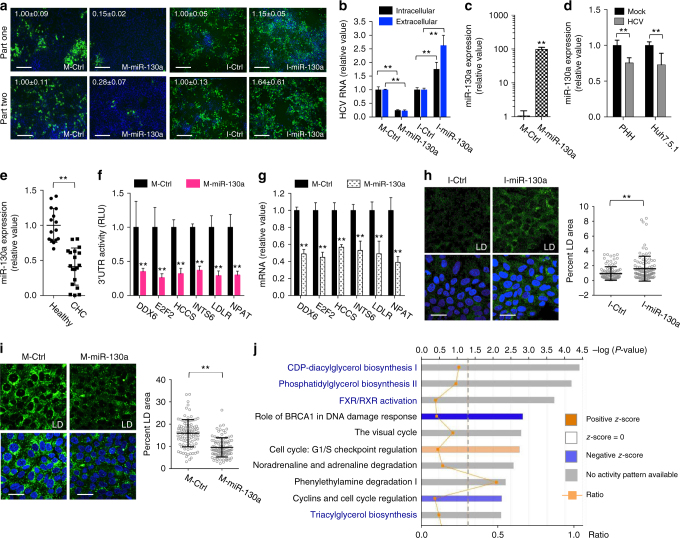
Fig. 6.
Identification of miR-130a that restricts HCV RNA replication and assembly. a, b miR-130a mimic or inhibitor transfection in Huh7.5.1 cells inhibits or enhances HCV infection, respectively. a Part-one and part-two HCV core protein expression were determined by immunostaining. Green, HCV core; blue, nuclei. Scale bars, 100 μm. b Levels of intracellular and extracellular HCV RNA were measured by Q-PCR. c Transfection efficiency of miR-130a mimic overexpression in Huh7.5.1 cells. d HCV infection decreases miR-130a expression in Huh7.5.1 cells and PHH. e Comparison of hepatic miR-130a abundance between liver samples of CHC patients and those of healthy controls. f, g miR-130a mimic transfection inhibits 3′-UTR activities (f) and mRNA levels (g) of various predicted cellular targets in Huh7.5.1 cells. h, i Representative images and quantitative analyses of LD contents in Huh7.5.1 cells transfected with control or miR-130a inhibitor (h) or mimic (i). Green, LDs, stained by BODIPY; blue, nuclei. Scale bars, 100 μm. 100 cells under each indicated condition were counted and percentages of LD area were measured. i Cells were treated with oleic acid (40 μM) for 24 h before being stained for LD contents. j Bioinformatics-based pathway analysis was conducted for miR-130a downregulated genes (Supplementary Data 7) using IPA. Values are normalized relative to Ctrl, and error bars represent SD of the mean, n = 3 (a–d, g) or 5 (f). **P < 0.01 determined by Student’s t-test