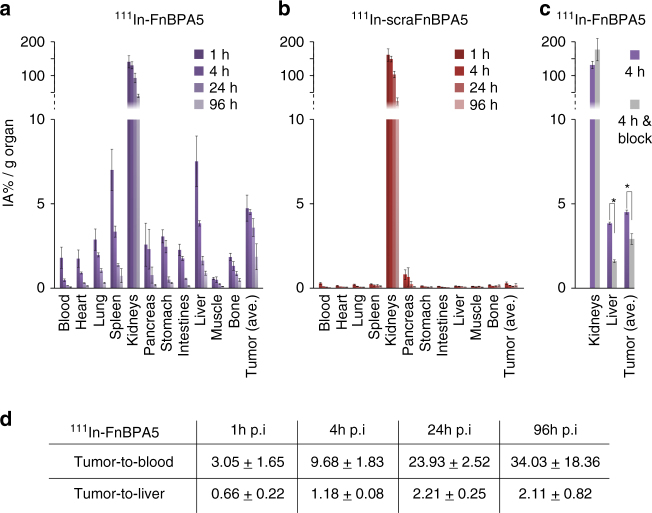
Fig. 6.
Biodistribution and blocking study of radiolabeled 111In-FnBPA5 and 111In-scraFnBPA5. a The biodistribution of 111In-FnBPA5 in PC-3-bearing mice was monitored at different time points in various organs. b The biodistribution of 111In-scraFnBPA5 was monitored in the same way. 111In-FnBPA5 (violet) showed a significant higher uptake than 111In-scraFnBPA5 (red) in all organs except for the kidneys, confirming the Fn-specificity of the accumulation. c Blocking studies were performed and the uptake was analyzed 4 h post injection (p.i.). The blocking of the binding sites via the pre-injection of unlabeled FnBPA5 caused a significant reduction in the uptake of 111In-FnBPA5 in both liver and tumor (*p < 0.05, Student’s t test, n = 4), whereas it did not change the uptake in the kidneys. The blocking showed a higher influence on 111In-FnBPA5 uptake in the liver than in the tumor, suggesting the presence of more binding sites (fibronectin) in the tumor. d The higher retention time of 111In-FnBPA5 in the tumor is reflected in increasing tumor-to-blood and tumor-to-liver ratios with increasing time. Bars represent means with error bars being standard deviations