Figure 2.
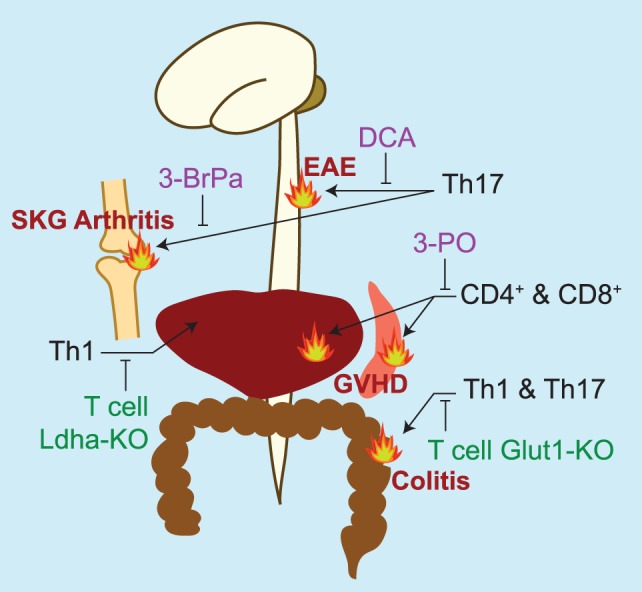
Summary of studies targeting glycolytic machinery in vivo to treat pathologies with prominent inflammatory T cell contributions. Pharmacologic inhibitors of glycolysis are listed in purple. DCA, dichloroacetate, an inhibitor of pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (12); 3-BrPa, 3-bromopyruvate, an inhibitor of hexokinase and GAPDH (93); 3-PO, 3-(3-pyridinyl)-1-(4-pyridinyl)-2-propen-1-one, an inhibitor of 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-bisphosphatase 3 (PFKFB3, PFK2) (91). Genetic models targeting glycolytic machinery in T cells are listed in green. LDH-A, lactate dehydrogenase A (79); Glut-1, glucose transporter 1 (90). In vivo models of inflammation studied are experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE)—a murine model of multiple sclerosis, SKG arthritis [a model of rheumatoid arthritis that spontaneously develops in the SKG strain of mice (99)]; graft versus host disease (GVHD), and colitis.
