Figure 2.
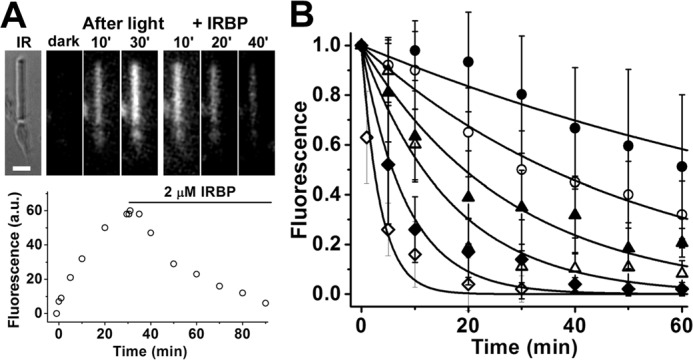
Measurement of all-trans-retinol removal by different concentrations of IRBP in isolated metabolically intact rod photoreceptors from wild-type mice. A, removal of all-trans-retinol formed after bleaching by 2 μm IRBP. IR, infrared image of a single rod photoreceptor showing its straight outer segment over the rounded tapered inner segment; bar, 5 μm. Bleaching was carried out between t = −1 min and t = 0; IRBP was added 30 min after bleaching. Fluorescence images of the cell were acquired with 360 nm excitation and >420 nm emission. B, removal of all-trans-retinol by different concentrations of IRBP added at t = 0, 30 min after the bleaching of rhodopsin. Retinol outer segment fluorescence intensities have been normalized over the value at t = 0. The lines are simple exponentials, e−k·t, decaying to 0 with unitary amplitude at t = 0 min; they have been drawn with rate constants k determined from the experimental data points. Without addition of IRBP, retinol fluorescence decreased with a rate constant 0.009 ± 0.001 min−1 (●, n = 8). IRBP concentrations and removal rate constants are, in μm and min−1, respectively: 1, 0.020 ± 0.001 (○, n = 6); 2, 0.036 ± 0.003 (▴, n = 7); 5, 0.06 ± 0.01 (▵, n = 7); 10, 0.12 ± 0.02 (♦, n = 8); 20, 0.29 ± 0.05 (♢, n = 8). Error bars represent standard deviations. The errors for the removal rate constants were obtained from the curve fits.
