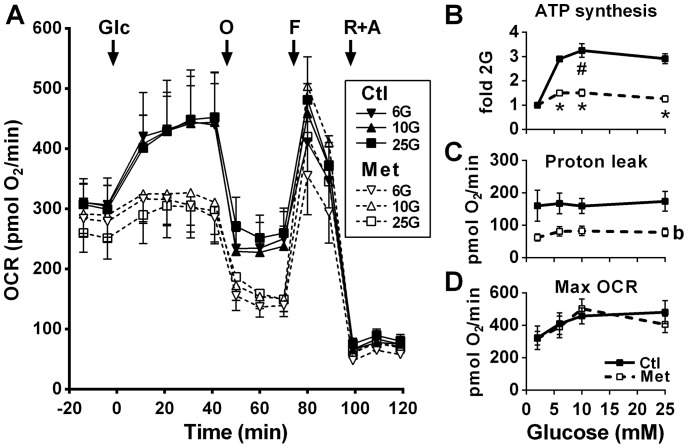
Figure 3.
Effect of glucose on mitochondrial respiration in the absence and presence of metformin. OCR was recorded in INS1 (832/13) cells treated with 5 mm metformin (Met) or vehicle (Ctl). Additions of glucose (Glc) were made from 2 mm to reach 2, 6, 10, or 25 mm glucose (G). At the indicated time, 0.25 μm oligomycin (O), 5 μm FCCP (F), and 1 μm rotenone plus 0.1 μm antimycin (R+A) were added. A, OCR profile. B, ATP turnover (glucose effect on OCR attributed to ATP production) calculated as change between rate 5 (fifth time point in A) and the average of rates 8 and 9 and expressed as fold over the 2 mm glucose condition of the same treatment (± metformin). C, proton leak calculated as change between averages of rates 8–9 and rates 12–14. D, maximal OCR recorded after FCCP addition (rate 10). In A, the traces at 2 mm glucose that remained stable after glucose addition have been omitted for clarity. The results are expressed as means ± S.E.; n = 4–6 from 2 separate experiments. Two-way ANOVA with Sidak's multiple comparisons test was used. #, p < 0.05 for glucose effect from 2 to 10 mm glucose in the control condition; *, p < 0.05 for metformin effect versus control at a given glucose concentration; b, p < 0.0001 for overall metformin effect.