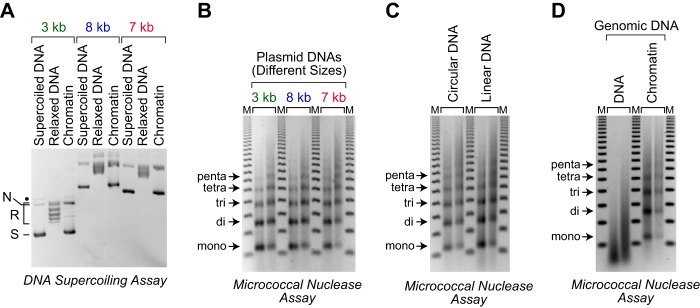
Figure 3.
Assembly of various DNA templates with the dNLP-ISWI system. A, DNA supercoiling analysis shows the efficient assembly of three different plasmid DNAs. Chromatin assembly reactions were carried out with three plasmid DNAs: pGIE-0 (3 kb) (50), which contains sequences from the adenovirus E4 promoter; pJH187 (8 kb), which contains sequences from the Drosophila Antennapedia gene; and pLA4 (7 kb) (51), which contains sequences from bacteriophage T4. Chromatin assembly and analysis were performed as described in the legend for Fig. 1B, except that native Drosophila core histones were used instead of recombinant Drosophila core histones. B, partial MNase digestion analysis reveals the assembly of periodic nucleosome arrays on three different plasmid DNAs. Reactions were performed as described in A, and the samples were analyzed as described in the legend for Fig. 1C. C, chromatin can be assembled with either circular or linear DNA. Reactions were performed as described in A, with relaxed circular or linearized pLA4 (7 kb), and the resulting samples were subjected to partial MNase digestion analysis. D, the dNLP-ISWI system can be used for the assembly of genomic DNA into periodic nucleosome arrays. Chromatin assembly reactions were carried out as described in A with native calf thymus genomic DNA that is mostly greater than 10 kb in length (supplemental Fig. S3). The chromatin (right) and genomic DNA (left) were subjected to partial MNase digestion analysis in parallel.