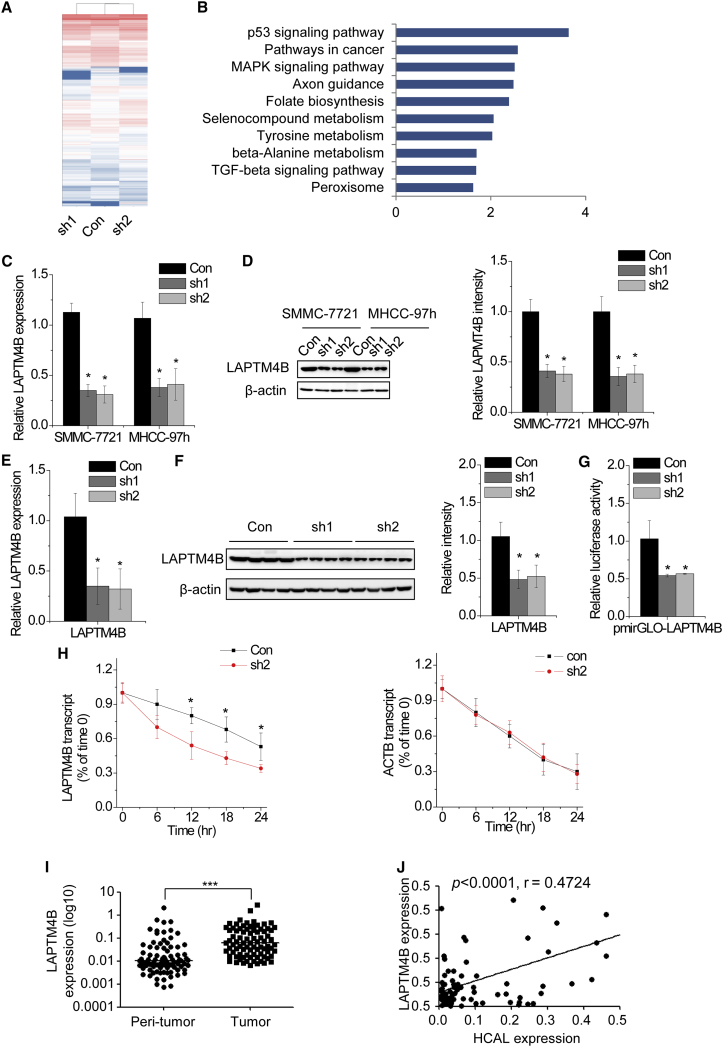
Figure 4.
LAPTM4B Is the Target Gene of HCAL
(A) Expression heatmap of transcripts regulated by HCAL (fold change > 2; p < 0.05). Red and blue indicate upregulation and downregulation, respectively. (B) The top 10 pathways affected by HCAL downregulation according to the KEGG analysis. (C) Relative LAPTM4B mRNA expression in control and HCAL-knockdown cells was determined by performing qPCR. (D) Left, LAPTM4B protein levels in control and HCAL-knockdown cells were determined by performing western blotting. Right, quantification of LAPTM4B protein levels. (E) LAPTM4B mRNA expression in the xenografts of nude mice injected with HCAL-knockdown cells analyzed by qPCR. (F) Left, LAPTM4B protein levels in the xenografts of nude mice injected with HCAL-knockdown cells was analyzed by performing western blotting. Right, quantification of LAPTM4B protein levels. (G) Relative luciferase activity of LAPTM4B 3′ UTR in control and HCAL-knockdown SMMC-7721 cells. Data are presented as the relative ratio of firefly luciferase activity to Renilla luciferase activity. (H) Stability of LAPTM4B and ACTB mRNA over time was measured by performing qPCR relative to time 0 after blocking new RNA synthesis with α-amanitin (50 mM) in SMMC-7721 cells expressing control and HCAL shRNAs and was normalized to that of 18S rRNA (a product of RNA polymerase I that is unaffected by α-amanitin). (I) LAPTM4B expression in 84 pairs of HCC and corresponding peritumor tissues was analyzed by qPCR. (J) Correlation between HCAL and LAPTM4B mRNA levels in the same set of 84 HCC tissues was determined using Pearson’s correlation analysis. Data are expressed as mean ± SD; *p < 0.05 and ***p < 0.001.