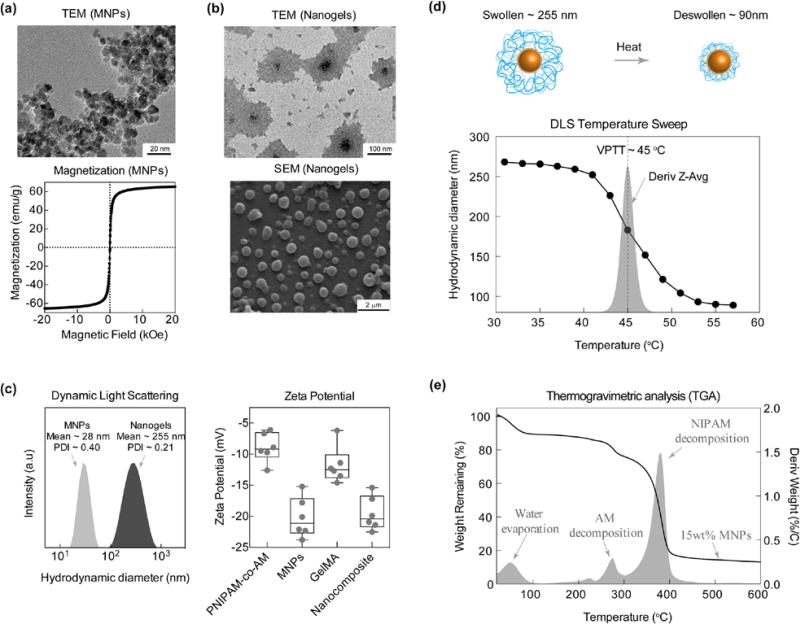
Figure 2.
MNPs and Nanogel Characterizations. (a) TEM and SQUID characterization of MNPs revealing uniform size and superparamagnetic behavior respectively. (b) TEM and SEM of poly(NIPAM-co-AM)/MNP nanogels. (c) DLS comparing sized distribution of MNPs to poly(NIPAM-co-AM)/MNP nanogels. MNPs show a mean hydrodynamic diameter of 28 nm with a PDI of 0.40 while nanogels show a mean of 255 nm with a PDI of 0.21. (d) VPTT was determined to be 45°C from a temperature derivative of Dh.(e) TGA provides copolymer determination of approximately 80:20 (PNIPAM:AM) and MNP approx. 15 wt.%. Zeta potential of individual polymers compared to MNPs and nanocomposites demonstrates increased stability of nanocomposite.