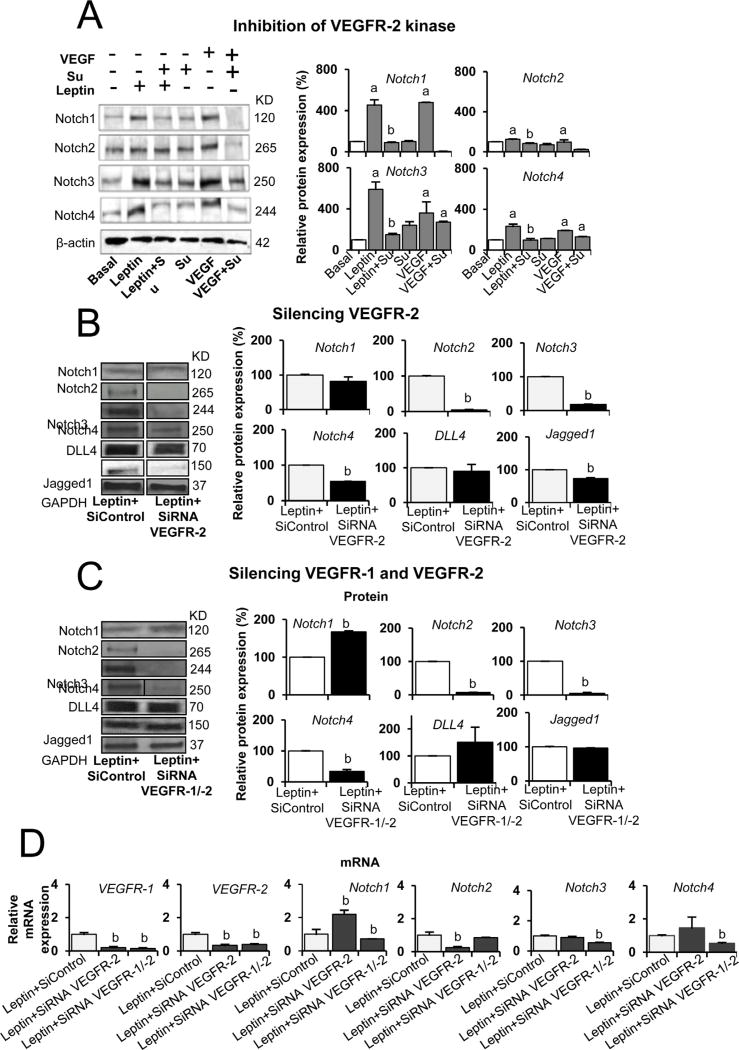
Fig. 6. Inhibition of kinase activity and knockdown of VEGF receptors decrease leptin induction of Notch expression in endothelial cells.
A. Leptin induction of Notch receptors in HUVEC requires VEGFR2 kinase activity. Western blot representative results from the reduction of leptin-induced Notch receptors via VEGFR kinase inhibition. HUVEC were treated for 24 h with leptin (1.2 nM), VEGFR-2 inhibitor SU5416 (5 µmol/l) and positive control VEGF (25 ng/ml). B. Leptin induction of Notch proteins in HUVEC requires VEGFR-2 gene activity. Represented here are western blot results from the reduction of leptin-induced Notch via VEGFR-2 SiRNA knockdown. Results show the effects of VEGFR-2 SiRNA (1 µg) after 6 h on leptin-induced expression of Notch receptors and ligands in HUVEC. C. Leptin induction of Notch proteins in HUVEC is reduced by knockdown of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 gene activities. Western blot representative results from the reduction of leptin-induced Notch via VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 SiRNA knockdown. D. Leptin induction of Notch mRNA in HUVEC is reduced by knockdown of VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 gene activities. Quantitative results from real-time PCR of Notch, VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 mRNA expression in HUVEC treated with leptin and VEGFR-1 and VEGFR-2 SiRNA. Beta-actin or GAPDH were used as loading controls. Relative protein expression was calculated as percentage to basal. Histograms show densitometric analysis of Notch protein expression using NIH image J software. RNA expression was calculated by normalizing values to GAPDH mRNA. Relative mRNA expression was calculated to basal. Data is presented as an average ± s.d. from three independent experiments. Su: SU5416; SiControl: siRNA control. a: p<0.05 when compared to basal. b: p<0.05 when compared to endothelial cells treated with leptin.