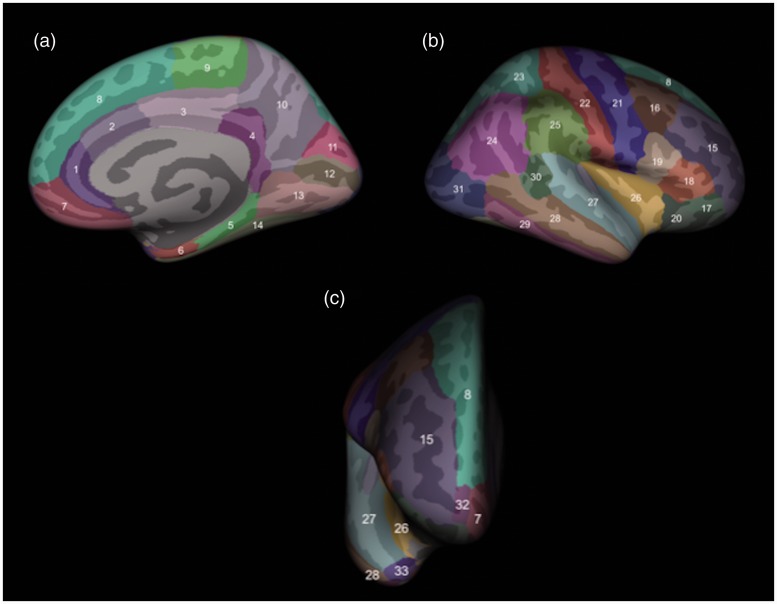
Figure 1.
Assessment of cortical thickness in brain areas, as shown in this three-dimensional rendering from medial (a), lateral (b) and frontal (c) views. The cortical structures assessed, delineated by FreeSurfer, were the rostral (1) and caudal (2) anterior cingulate gyrus, posterior cingulate gyrus (3), isthmus of the cingulate gyrus (4), parahippocampal gyrus (5), entorhinal cortex (6), medial orbitofrontal cortex (7), superior frontal gyrus (8), paracentral lobule (9), precuneus (10), cuneus (11), pericalcarine cortex (12), lingual gyrus (13), fusiform gyrus (14), rostral (15) and caudal (16) middle frontal gyrus, pars orbitalis (17), pars triangularis (18) and pars opercularis (19) of the inferior frontal gyrus, lateral orbitofrontal cortex (20), precentral gyrus (21), postcentral gyrus (22), superior (23) and inferior (24) parietal cortex, supramarginal gyrus (25), insular cortex (26), superior temporal gyrus (27), middle temporal gyrus (28), inferior temporal gyrus (29), banks of the superior temporal sulcus (30), lateral occipital cortex (31), frontal pole (32) and temporal pole (33).