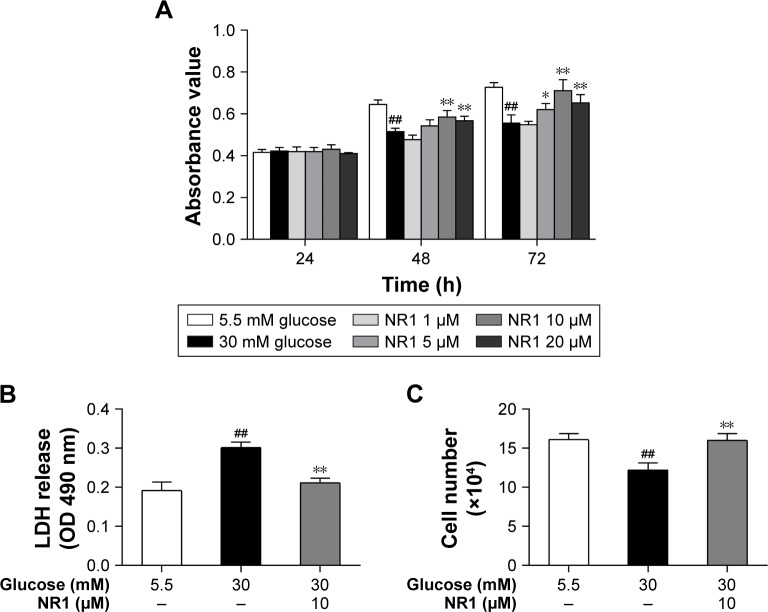
Figure 2.
Protection of NR1 from high glucose-induced cytotoxicity.
Notes: Rat RCECs were incubated with varying concentrations of NR1 (1, 5, 10 and 20 μM) in 30 mM glucose. The medium containing 5.5 mM glucose was used as a control. After culturing for 24, 48 or 72 h, MTT was used to examine cell viability. The MTT assay showed that 5, 10 and 20 μM NR1 increased cell viability after 48 and 72 h (A). After culturing for 72 h, LDH release and trypan blue staining assays were performed to examine cell cytotoxicity. The LDH assay showed that 10 μM NR1 significantly decreased the cellular LDH release (B). The trypan blue assay showed that 10 μM NR1 increased the live cell count in rat RCECs (C). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n=3). ##P<0.01 versus 5.5 mM glucose; **P<0.01 and *P<0.05 versus 30 mM glucose.
Abbreviations: LDH, lactate dehydrogenase; NR1, Notoginsenoside R1; RCECs, retinal capillary endothelial cells.