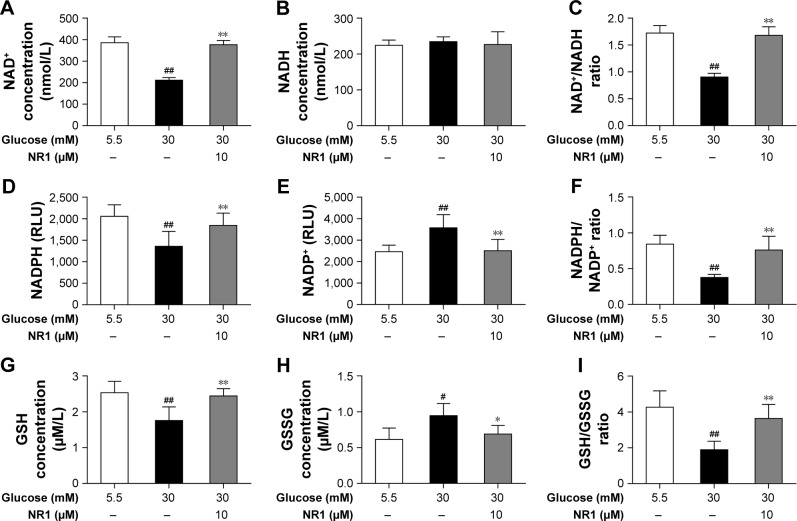
Figure 6.
NR1, an intracellular redox modulator, is useful under high glucose conditions when the intracellular redox status is impaired.
Notes: RCECs were incubated with 10 μM NR1 in 30 mM glucose for 72 h. The medium containing 5.5 mM glucose was used as a control. High glucose induced excess ROS production that impaired the antioxidant system and thereby disturbed redox homeostasis. This phenomenon subsequently led to imbalance in NAD+/NADH and NADPH/NADP+ ratios, promoted GSH oxidation and attenuated GSSG reduction. Treatment with NR1 increased the ratios of NAD+/NADH and NADPH/NADP+ in rat RCECs (A–F). In parallel, NR1 administration increased the GSH/GSSG ratio, which improved the redox status (G–I). Data are expressed as the mean ± SD (n=3). ##P<0.01 and #P<0.05 versus 5.5 mM glucose; **P<0.01 and *P<0.05 versus 30 mM glucose.
Abbreviations: GSH, glutathione; NAD+, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+; NR1, Notoginsenoside R1; RCECs, retinal capillary endothelial cells; ROS, reactive oxygen species.