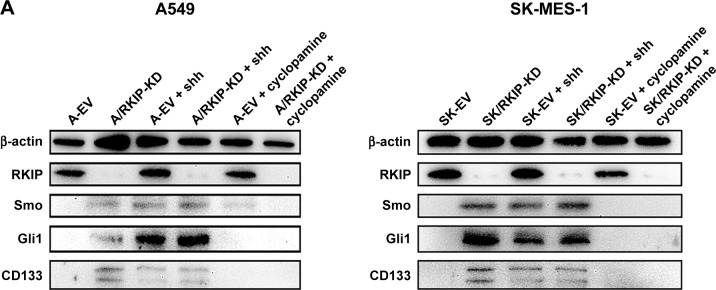
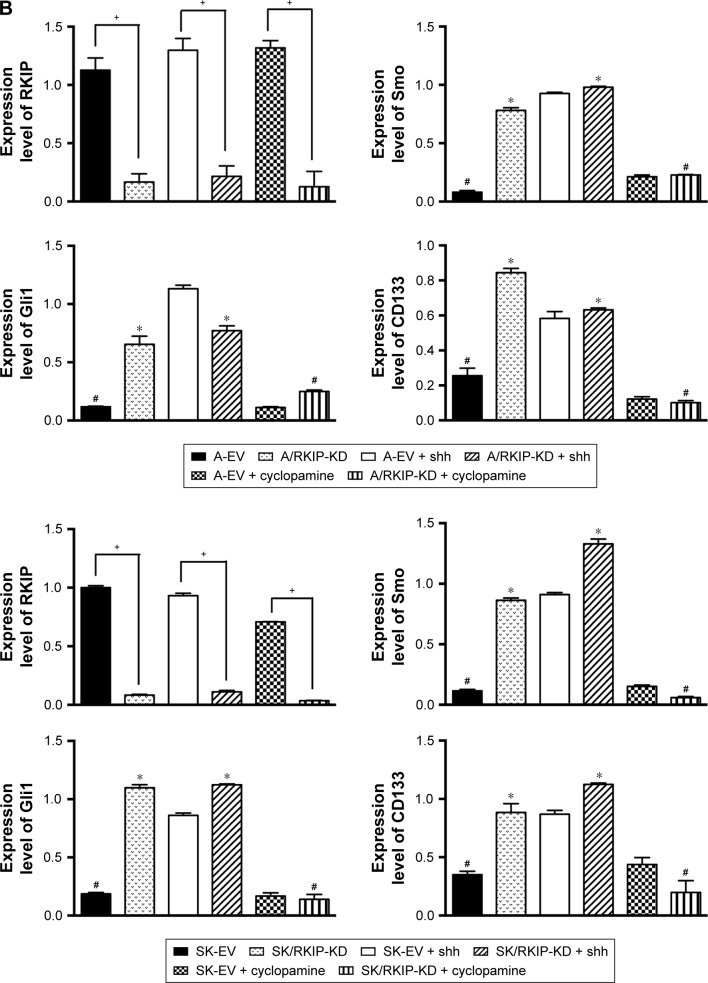
Figure 6.
RKIP reduction enhances Shh–Gli1 signaling and increases CD133 expression in NSCLC cell lines.
Notes: (A) Representative Western blot results show the expression levels of RKIP, Smo, Gli1 and CD133 in A/RKIP-KD, SK/RKIP-KD and the corresponding control cell lines A-EV and SK-EV; the results when these cell lines were treated with N-shh and cyclopamine are also shown. β-actin was used as a loading control. (B) Histograms show the relative expression levels of RKIP, Smo, Gli1 and CD133 in the cells by grayscale analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. +P<0.05 vs cells transfected with empty vectors; *P<0.05 vs cells transfected with empty vectors; #P<0.05 vs cells with RKIP knockdown. All experiments were performed in triplicate.
Abbreviations: EV, empty vector; KD, knockdown; NSCLC, non-small-cell lung cancer; RKIP, Raf kinase inhibitor protein; A-EV, A549 cells transfected with empty vector; A/RKIP-KD, A549 cells transfected with RKIP-knockdown vector; SK-EV, SK-MES-1 cells transfected with empty vector; SK/RKIP-KD, SK-MES-1 cells transfected with RKIP-knockdown vector.