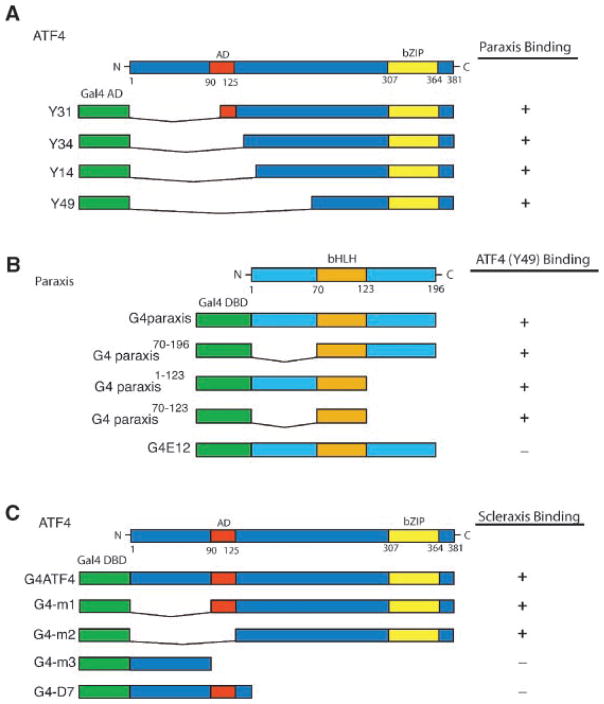
Fig. 1.
Domain mapping of ATF4, paraxis, and scleraxis for sites of interaction. A yeast-2-hybrid screen with deletion mutant constructs and full-length activation domain partner listed in the right column, with (+) indicating positive yeast growth and β-galactosidase (control) activity and (−) indicating no growth or β-galactosidase. A: ATF4 truncations that were identified in the initial yeast two hybrid screens along with full-length ATF4. Y49 which contains the bZIP motif was used as a bait with paraxis mutants. B: Paraxis mutants containing the bHLH domain (G4 paraxis) interactions with the Y49 ATF4 construct were assessed. E12 was used as a control to verify that the interaction with ATF4 is specific for the bHLH domain of paraxis. C: ATF4 mutants (Ord and Ord, 2003) containing the bZip region (m1 and m2) lacking the bZip region (m3 and D7) and interactions with scleraxis were assessed. Data are from three separate experiments with three replicates per experiment.